Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHow researchers flinging salmon inadvertently spurred tree growth
Scientists studying salmon in Alaska flung dead fish into the forest. After 20 years, the nutrients from those carcasses sped up tree growth.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYoung people’s memories improved when they stopped using marijuana
After just a week of not using pot, teens’ and young adults’ abilities to remember lists of words got better, a small study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIf you want to believe your home’s bug free, don’t read this book
‘Never Home Alone’ reveals the hidden world living in human-made spaces.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient South Americans tasted chocolate 1,500 years before anyone else
Artifacts with traces of cacao push back the known date for when the plant was first domesticated by 1,500 years.
By Bruce Bower -
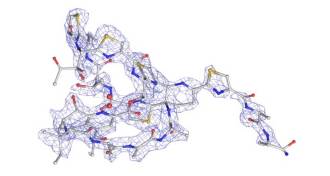 Chemistry
ChemistryZapping substances with electrons can quickly map chemical structures
Speedy molecular identification originally developed for proteins might benefit crime lab researchers and drugmakers.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Animals
AnimalsWhile eating, these tiny worms release chemicals to lure their next meal
As they eat insects, one nematode species releases chemicals that attract more insect prey.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Animals
AnimalsCoral larvae survive being frozen and thawed for the first time
Cryopreservation might help save some coral reefs at risk from climate change and other dangers.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThe first vertebrates on Earth arose in shallow coastal waters
After appearing about 480 million years ago in coastal waters, the earliest vertebrates stayed in the shallows for another 100 million years.
-
 Life
LifeTo get a deeper tan, don’t sunbathe every day
Skin cells make protective melanin on a 48-hour cycle.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a snake named Hannibal led to a discovery about cobra cannibalism
Scientists discovered that cobras in southern Africa eat each other more often than thought. And that may be true for cobras in other places as well.
-
 Plants
PlantsLiverwort plants contain a painkiller similar to the one in marijuana
Cannabinoids found in liverwort plants could spell relief for those suffering from chronic pain.
-
 Life
LifeWhy some people may be more susceptible to deadly C. difficile infections
Proline, a type of amino acid, increases when gut microbe mixes are disturbed, giving this pathogen a ready food source.