Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSalamander ancestors could regenerate limbs
Salamanders and ancient amphibians share similar way of regenerating limbs.
-

-
 Animals
AnimalsAs panda baby grows, mom’s milk changes
In the first month after a mama panda gives birth, her milk changes in composition, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHowler monkeys sacrifice sperm for deeper roars
In howler monkeys, expanded vocal tracts make for deeper-voiced males with smaller testes, researchers find.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSigns of Alzheimer’s seen in young brain’s GPS cells
Signs of Alzheimer’s can show up in the brain’s compass decades before symptoms strike.
By Meghan Rosen -
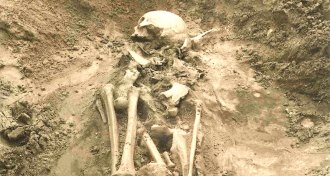 Anthropology
AnthropologyPlagues plagued the Bronze Age
Ancient bacterial DNA provides first clues to Bronze Age plagues in Europe and Asia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive species may be great snacks for predators
The arrival of a new food source can benefit predators, a new study finds. But if there are no native species around to eat, it’s a different story.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFurry, spiky mammal scampered among dinosaurs
Early Cretaceous fur ball with spikes discovered in Spain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor glowworms, the brightest girls get the guy
Brighter female glowworms attract more mates and lay more eggs than their dimmer peers.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPentaquarks, locked-in syndrome and more reader feedback
Readers discuss pentaquark sightings, delightful diatoms and whether an ancient four-legged fossil was actually a snake.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAsian tiger mosquito genome sequenced
Researchers have sequenced the genome of the Asian tiger mosquito, a stealthy invasive species and carrier of tropical diseases.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow architecture can make ants better workers
The right nest architecture can make harvester ants better at their job, new research shows.
By Susan Milius