Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsJust when you thought snails couldn’t get any smaller…
Snails may not be speedy, but itty-bitty snail shells found in Borneo are breaking a size record at a breakneck pace.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsMarsh grass masquerades as a native species
The abundant cordgrass found in South American marshes may actually have invaded the region more than two centuries ago, a new study concludes.
-
 Animals
Animals‘On the Wing’ chronicles origins of flying animals
In "On the Wing," a biomechanicist reviews how animals took to the air.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthNew fascination with Earth’s ‘Boring Billion’
The Mesoproterozoic era, known as the boring billion, had very low oxygen, but it set the stage for the evolution of animals.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPetite primate fossil could upend ideas about ape evolution
Ancient fossils suggest modern apes descended from a small, gibbonlike creature.
By Bruce Bower -
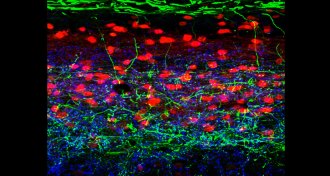 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceItch-busting nerve cells could block urge to scratch
A group of nerve cells in the spinal cord keep mechanical itch in check.
-
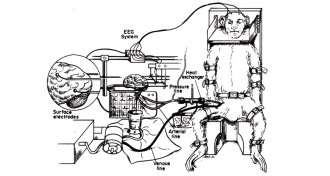 Neuroscience
Neuroscience1960s dog brain transplant was not followed by human studies
A pioneering study to transplant a dog’s brain led to later work on a monkey, but ethical considerations and technical know-how have prevented further work.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWildfires are an unexpected threat to California condors
Lead poisoning remains a threat to California condors, but a new review finds that wildfires may also be a danger to the big birds.
-
 Life
LifeHow electric eels put more zip in their zap
With feisty prey, an electric eel curls its tail to intensify shocks and exhaust prey.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeRare reptile holds clue to penis evolution
Preserved Victorian specimens reveal budding embryonic penis that disappears before adulthood.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeCats versus viruses: Arms race goes back millennia
A special protein has been protecting cats from feline AIDS for at least 60,000 years, genetic analysis suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCat-versus-virus arms race goes back millennia
Researchers have found evidence of an ancient arms race between Felis silvestris catus, the species familiar today as the domestic cat, and feline immunodeficiency virus.