Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
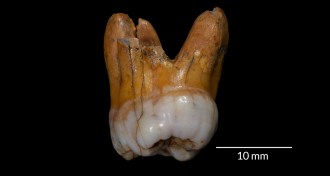
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
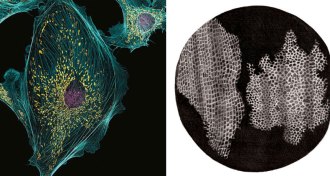
LifeMicroscopes have come a long way since 1665
A 350-year-old drawing in Robert Hooke’s Micrographia and an award-winning photo demonstrate the evolution of the microscope.
By Andrew Grant -
 Genetics
GeneticsNew catalog of human genetic variation could improve diagnosis
Study of human protein-coding variation reveals which genes are more likely to be involved in genetic diseases.
-
 Life
Life‘Racing Extinction’ documents plight of endangered species
The new documentary "Racing Extinction" offers hope that people can halt the sixth mass extinction.
-
 Neuroscience
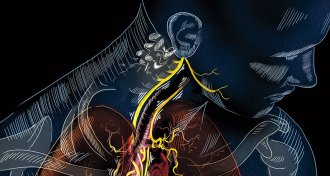
NeuroscienceViva vagus: Wandering nerve could lead to range of therapies
Researchers are testing ways to stimulate the vagus nerve to treat a slew of ailments.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMummified boy’s DNA unveils new but ancient maternal lineage
An Inca child’s DNA shows he hailed from a newly identified line of maternal ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsTortoises provide a window into the illegal wildlife trade
Tens of thousands of Indian star tortoises are poached every year, a new study finds.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHoneybees sweetened early farmers’ lives
Residue on pottery pegs ancient farmers as devotees of honeybee products.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies to fight Alzheimer’s may have unexpected consequences
Alzheimer’s-targeted antibodies make neurons misbehave even more, a study of mice shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWindy days mean smaller meals for little penguin chicks
Wind speed appears to affect how much food little penguins can bring home for their chicks.
-
 Life
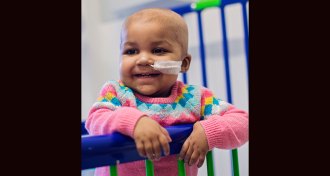
LifeGene editing helps a baby battle cancer
Doctors used molecular scalpels to tweak T cells to target leukemia but not harm the patient.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominids used wooden spears to fend off big cats
Saber-toothed cat remains suggest ancient hominids used wooden spears as defensive weapons.
By Bruce Bower