Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Plants
PlantsPretty flower uses dead arthropods to lure protectors
A sticky columbine from California lures arthropods to their death to lure protectors to the plant, a new study suggests.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyLong-necked monsters roamed more than Scotland’s lochs
The discovery of sauropod footprints in Scotland suggest the dinosaurs lived in lagoons.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsCan DNA predict a face?
DNA-based facial sketches are moving into the crime-solving arena. With current science, predictions of some features are better than others.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsInside the roaring sex lives of howler monkeys
Listening to the intense roars of howler monkeys in Mexico inspired scientists to decipher how and why calls differ among species.
-
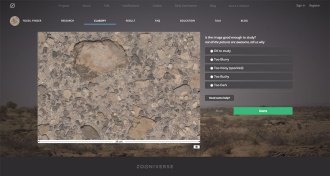 Archaeology
ArchaeologySearch for fossils from the comfort of home
The citizen science website FossilFinder.org lets anyone with an Internet connection look for fossils and characterize rocks at Kenya’s Lake Turkana Basin
By Erin Wayman -
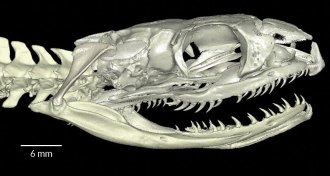 Animals
AnimalsSnakes evolved from burrowing ancestor, new data suggest
A new X-ray analysis of inner ears is the latest to weigh in on whether modern snakes descended from a burrowing or a swimming reptile.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsMystery deepens for what made tarantulas blue
Blue hair on tarantulas shows what evolution does with iridescence that females probably don’t care about.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsFor a python, every meal is like Thanksgiving
Burmese pythons rarely eat, but when they do, they gorge. Unlike humans, pythons have adaptations that allow them to survive on huge meals.
-
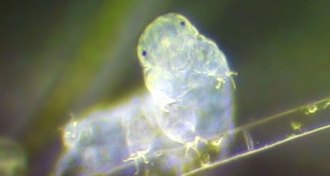 Genetics
GeneticsWater bears are genetic mash-ups
Drying out may help tardigrades soak up new DNA, which in turn aids the water bears in withstanding stress.
-
 Life
LifeDNA doubled in conifer ancestors
The genomes of conifers — pine, cypress and yew trees — doubled twice in the distant past.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTaste is all in your head
By targeting certain nerve cells in a mouse’s brain, scientists made plain water turn bitter or sweet.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGut microbes signal when dinner is done
Helpful E. coli bacteria that live in the guts of animals produce proteins that can decrease an animal’s appetite only 20 minutes after receiving nutrients