Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Plants
PlantsSingle gene influences a petunia’s primary pollinator
Mutations on a single gene determine how much ultraviolet light a petunia flower absorbs, and in turn, which animal pollinates the flower.
-
 Life
LifeTo push through goo, use itty, bitty propellers
Newly designed micropropellers mimic bacteria to move through viscous surroundings.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew movie asks viewers to care about whale hunters. Will they?
A new movie tells the tale of sailors shipwrecked by a whale. But it’s hard to feel sorry for the people trying to kill the animal.
-
 Life
LifeMicrobes show up on schedule after death
Microbes in the soil beneath dead bodies offer forensic clues for time and place of death.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
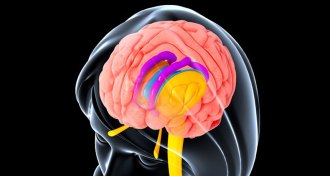
NeuroscienceBrain shapes come from mom and dad
By linking genes to brain shapes, scientists have a new way to study how the brain works.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome warblers make their long winter migration even longer
Blackpoll warblers in western North America head east to fatten up before their transoceanic migration.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPlayful pups conceived via in vitro fertilization for the first time
Scientists have solved the mystery of how to perform in vitro fertilization in dogs, which could help rid canines of heritable diseases.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsLiberia’s Ebola outbreak largely traced to one source
Ebola’s spread and evolution in Liberia echoes patterns seen in Sierra Leone.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBusy eyes can make ears go temporarily deaf
When challenged with a tough visual task, people are less likely to perceive a tone, suggesting that perceptual overload can jump between senses.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEyes hard at work can make ears go temporarily deaf
When challenged with a tough visual task, people are less likely to perceive a tone, suggesting that perceptual overload can jump between senses.
-
 Animals
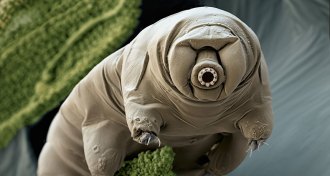
AnimalsWater bears’ genetic borrowing questioned
A new analysis of tardigrade DNA suggests that water bears don’t swap many genes with other organisms after all.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor male peacock spiders, the best dancers get the girl
Male peacock spiders dance to attract the ladies. And those that perform the best get the girl, a new study finds.