Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBubbles may have sheltered Earth’s early life
Bubbles formed on ancient shorelines offer scientists a new place to look for traces of early life.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnatomy of the South Korean MERS outbreak
The Middle East respiratory syndrome virus, which infected 186 people in South Korea in 2015, quickly spread within and between hospitals via a handful of “superspreaders.”
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNumber of wild bees drops where they’re needed most
Wild bee abundance in the United States is lowest in agricultural regions, according to a new model.
-
 Life
LifeTweaking the pattern equations
A more than 60-year-old theory about how patterns in nature form gets an update.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFog ferries mercury from the ocean to land animals
Scientists have traced mercury in the waters of the Pacific Ocean to animals, including mountain lions, in California.
-
 Life
LifeUpending daily rhythm triggers fat cell growth
Constant production of stress hormone spurs fat growth.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRoosters run afoul of genetic rules
Moms aren’t always the only ones that pass mitochondrial DNA to offspring, a study of chickens finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
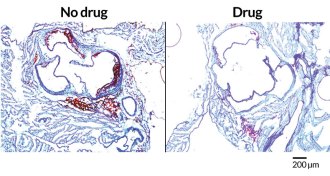
Health & MedicineTo treat the heart, start with the gut
Preventing gut bacteria from making certain chemical compounds reduced artery clogging in mice, researchers report.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMale monkeys go rouge for mating season
Bright red lip color separates players from bachelors during monkey mating season.
-
-
 Animals
AnimalsAlgal toxin impairs sea lion memory
California sea lions that have brain damage linked to domoic acid poisoning have impaired spatial memory, a new study finds.
-
 Life
LifeIn the body, cells move like flocks of birds or schools of fish
Cells move in groups similarly to flocks of birds and schools of fish