Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyClimate, new physics and Jupiter on the horizon for 2016
The first issue of the new year features stories about what will, editor in chief Eva Emerson predicts, hold on as scientific newsmakers during 2016.
By Eva Emerson -
 Climate
ClimateArctic passageways let species mingle
People aren’t the only animals likely to use passages that open up as the Arctic melts.
By Susan Milius -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsDark matter helped destroy the dinosaurs, physicist posits
In ‘Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs,’ Lisa Randall finds connections between particle physics, cosmology, geology and paleontology.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsAnts’ size and profession controlled by chemical tags on DNA
Epigenetic marks determine whether female Florida carpenter ants are soldiers or foragers.
-
 Paleontology
Paleontology12 amazing fossil finds of 2015
From an ancient sponge ancestor to the Carolina Butcher, scientists learned a lot about life on Earth this year.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsLemurs chat only with their best friends
Ring-tailed lemurs maintain friendships built with grooming by calling to each other, a new study finds.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThese truisms proved false in 2015
Don’t always believe what you hear. These truisms turned out to be false in 2015.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPuff adders appear ‘invisible’ to noses
The snakey scent of puff adders proves difficult for even sensitive animal noses to detect.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBubbles may have sheltered Earth’s early life
Bubbles formed on ancient shorelines offer scientists a new place to look for traces of early life.
By Meghan Rosen -
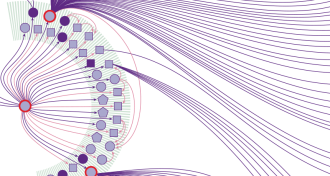 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnatomy of the South Korean MERS outbreak
The Middle East respiratory syndrome virus, which infected 186 people in South Korea in 2015, quickly spread within and between hospitals via a handful of “superspreaders.”
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNumber of wild bees drops where they’re needed most
Wild bee abundance in the United States is lowest in agricultural regions, according to a new model.
-
 Life
LifeTweaking the pattern equations
A more than 60-year-old theory about how patterns in nature form gets an update.