Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat really changes when a male vole settles down
Bachelor prairie voles can’t tell one female from another, but saying “I do” means more than just settling down.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsRaindrops help pitcher plants trap dinner
Pitcher plants use the force of falling raindrops to fling prey into their traps.
-
 Plants
PlantsStinky seeds dupe dung beetles
Seeds that look and smell like animal poop can trick dung beetles into spreading and burying the seeds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat happens to animals in a hurricane?
Hurricanes can be devastating to animals on land and in the sea, but they can also provide opportunities.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceKavli Foundation gives more money for the brain
The Kavli Foundation will provide $100 million toward solving the mysteries of the brain.
-
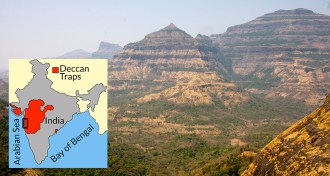 Earth
EarthGiant asteroid may have triggered deadly volcano eruptions
Increased volcanic eruptions coincided much more closely with an asteroid impact and the extinction of the dinosaurs than previously believed, a new study suggests.
-

-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyBronze Age mummies identified in Britain
Bone analysis finds widespread mummy making in ancient England and Scotland.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsThis may be the world’s tiniest snail
Tiny snail unearthed in China could be the world's smallest, researchers report.
-
 Life
LifeBabies low on key gut bacteria at higher risk of asthma
Asthma risk may be set early in life, but mice data suggest that the risk could altered by friendly gut bacteria.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome seabirds will be hit hard by sea level rise
Seabird species that nest on low-lying islands in stormy winter months could see huge losses as sea levels rise, a new study finds.
-
