Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
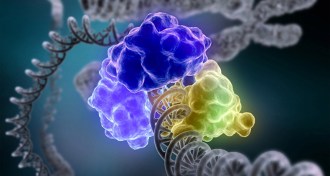
GeneticsChemistry Nobel honors studies of DNA repair mechanisms
Studies of DNA’s repair mechanisms have won Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar the 2015 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Sarah Schwartz and Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsNo eyes, no problem for color-sensing coral larvae
Switching colors of underwater light can switch preferences for where staghorn corals choose their forever homes.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansChimpanzees show surprising flexibility on two feet
Chimpanzees’ upper-body flexibility while walking upright suggests ancient hominids walked effectively.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsWhat really changes when a male vole settles down
Bachelor prairie voles can’t tell one female from another, but saying “I do” means more than just settling down.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsRaindrops help pitcher plants trap dinner
Pitcher plants use the force of falling raindrops to fling prey into their traps.
-
 Plants
PlantsStinky seeds dupe dung beetles
Seeds that look and smell like animal poop can trick dung beetles into spreading and burying the seeds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat happens to animals in a hurricane?
Hurricanes can be devastating to animals on land and in the sea, but they can also provide opportunities.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceKavli Foundation gives more money for the brain
The Kavli Foundation will provide $100 million toward solving the mysteries of the brain.
-
 Earth
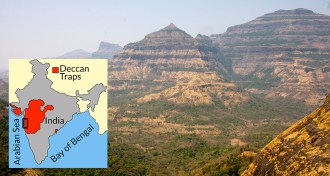
EarthGiant asteroid may have triggered deadly volcano eruptions
Increased volcanic eruptions coincided much more closely with an asteroid impact and the extinction of the dinosaurs than previously believed, a new study suggests.
-

-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyBronze Age mummies identified in Britain
Bone analysis finds widespread mummy making in ancient England and Scotland.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsThis may be the world’s tiniest snail
Tiny snail unearthed in China could be the world's smallest, researchers report.