Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsJumping conchs triumph at overheated athletics
“Simple” circulatory system outdoes fancier ones in delivering oxygen for jumping conchs in simulated climate change conditions.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsChemical tags on DNA appear to differ between gay and straight men
DNA marks distinguished homosexual men from heterosexual men with in a small twin study.
-
 Oceans
OceansWidespread coral bleaching threatens world’s reefs
The world’s corals are experiencing their third major bleaching event in 17 years.
-
 Humans
HumansInto Africa: Ancient skeleton sheds light on reverse migration
Ancient man’s DNA helps reveal extent of Eurasian farmers’ back-to-Africa migration some 3,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsFish have had telescoping jaws for 100 million years
Around 100 million years ago, fish developed a knack for extending their jaws to snare prey, and they’ve been perfecting this hunting technique ever since.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWeight and sun exposure linked to onset of multiple sclerosis
Among people with multiple sclerosis, those with higher body mass and lower adolescent sun exposure tended to be diagnosed with the disease at an earlier age, a new study suggests.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemistry Nobel granted for deciphering DNA repair
Three researchers win chemistry Nobel for working out how cells fix damaged genetic material
By Meghan Rosen and Sarah Schwartz -
 Animals
AnimalsHow the giraffe got its long neck
A new study of fossils suggests that the giraffe’s defining feature may have started evolving long before modern giraffes came on the scene.
-
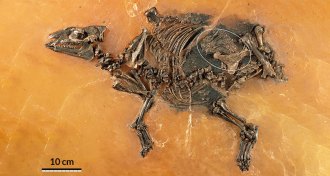 Animals
AnimalsOldest pregnant horselike fossil found
A 48-million-year-old fossil of an early horse and fetus is the oldest and best-preserved specimen of its kind.
-
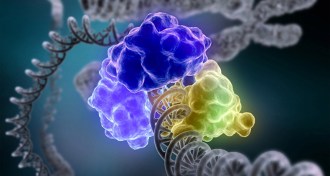 Genetics
GeneticsChemistry Nobel honors studies of DNA repair mechanisms
Studies of DNA’s repair mechanisms have won Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar the 2015 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Sarah Schwartz and Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsNo eyes, no problem for color-sensing coral larvae
Switching colors of underwater light can switch preferences for where staghorn corals choose their forever homes.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansChimpanzees show surprising flexibility on two feet
Chimpanzees’ upper-body flexibility while walking upright suggests ancient hominids walked effectively.
By Bruce Bower