Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-

-
 Life
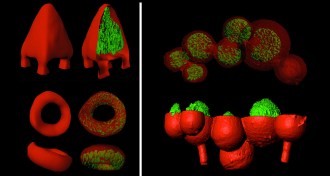
Life3-D printing builds bacterial metropolises
By simulating biofilms, new 3-D printing technique may help researchers study antibiotic resistance.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrainy videos
A short film that uses humor and science to explain congenital anosmia has won the Society for Neuroscience’s 2013 Brain Awareness Video Contest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMedicine Nobel goes to cellular transport research
Honor given to three scientists who discovered how machinery moves cargo around cells.
By Science News -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCellular transport research wins Nobel Prize in medicine or physiology
Guest post by Tina Hesman Saey and Nathan Seppa.
By Science News -
 Animals
AnimalsHiding up your nose is a clever strategy for ticks
Found hiding in the noses of Ugandan chimps, a new tick species hitchhiked its way to America in a researcher's nose.
-
 Life
LifeBlocking a hormone helps mice beat lengthy jet lag
A timekeeping brain molecule steadies the beat of the circadian clock, while stopping it allows for a quick reset.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCancer variants found in ‘neglected’ region of genome
Mutations outside of genes associated with disease in study using data from a thousand people.
-

-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSome grape-scented compounds repel mosquitoes
Molecules discovered to drive away bugs after researchers identify cells that detect, and are disgusted by, DEET.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTortoise-studying teen takes top Broadcom prize
Even a tortoise enthusiast can speed through a three-day gauntlet of science, engineering and math challenges to claim victory. River Grace, 14, of West Melbourne, Fla., did just that. At an awards ceremony October 1, he picked up the top award of $25,000. The teen was one of 30 finalists from 17 states who attended the third annual Broadcom Math, Applied Science, Technology and Engineering for Rising Stars, or MASTERS, competition.
By Science News -
 Plants
PlantsTiny fossils set record for oldest flowerlike pollen
Oldest flowerlike pollen might have come from an ancient relative of today’s flowering plants.
By Susan Milius