Neuroscience
-
 Life
LifeThe right mix of gut microbes relieves autism symptoms in the long run
Replacing missing gut microbes improves autism symptoms in children even two years later.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyIn research, detours are a key part of discovery
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the scientific process and the often contradictory research about Alzheimer's disease.
By Nancy Shute -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceVaginal microbes in mice transfer stress to their pups
During birth, microbes from a stressed mouse mother can carry some aspects of stress to her offspring.
-
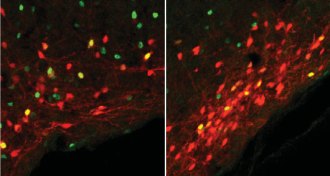 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNerve cells that help control hunger have been ID’d in mice
A mysterious bump on the human brain may be able to dial appetite up or down.
-
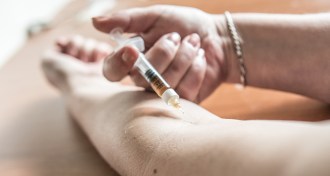 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA brain chemical tied to narcolepsy may play a role in opioid addiction
Long-term use of opioids such as heroin is linked to having more brain cells that release a chemical that regulates wakefulness and arousal.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWatch the brain jiggle with each heartbeat
A new twist on MRI can reveal how the brain wiggles.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow domestication changed rabbits’ brains
The fear centers of the brain were altered as humans tamed rabbits.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew studies add evidence to a possible link between Alzheimer’s and herpesvirus
Researchers saw higher levels of herpesvirus in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients, which may contribute to plaque formation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSplitting families may end, but migrant kids’ trauma needs to be studied
The long-term effects of separating children from their parents at the U.S. border need to be studied, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBees join an exclusive crew of animals that get the concept of zero
Honeybees can pass a test of ranking ‘nothing’ as less than one.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know — and don’t know — about a new migraine drug
A migraine prevention drug was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. But some questions about the therapy remain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHere’s why scientists are questioning whether ‘sonic attacks’ are real
Sonic attacks would be hard to pull off and a terrible way of incapacitating diplomats, experts say.