All Stories
-
 Humans
HumansHard throwers evolved a long time ago
Baseball hurlers provide clues to the ancient roots of bodies that can heave objects really fast.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsElephant diets changed millions of years before their teeth
The animals fed on grasses long before their molars could grind the tough plants.
By Erin Wayman -
 Astronomy
AstronomyCradled galaxies betray violent past
Hubble snaps ‘the Penguin’ and its egg-shaped companion.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineParalyzed rats relearn to pee
Bladder control restored for the first time in animals with stark spinal cord damage.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Chemistry
ChemistryHigh methane in drinking water near fracking sites
Well construction and geology may both play a role in pollution.
-
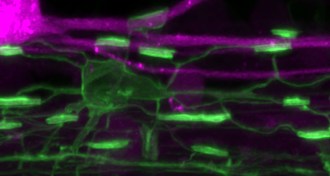 Life
LifeBrain cell insulators are short-timers
Limited myelin production time may make it harder to repair nerve casings damaged by multiple sclerosis.
-
 Earth
EarthCleaner air may have brought more storms
Pollution during the 20th century appears to have suppressed North Atlantic hurricanes.
-
 Math
MathA field where breakthroughs are hard to come by produces two big advances on a single day
Problems in number theory often have a certain exasperating charm: They are extraordinarily simple to state, but so difficult to prove that centuries of effort haven’t sufficed to crack them. So it’s pretty remarkable that on one day this May, mathematicians announced results on two of these mathematical conundrums. Both proofs address one of the […]
-

Battle of the deer and eagle
Camera trap solves mystery of deer downed without a trace.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsFirst four-quark particle may have been spotted
If confirmed, the tetraquark could shed light on how atomic nuclei are held together.
By Andrew Grant -
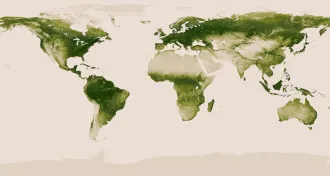 Earth
EarthSatellite captures Earth’s greenery
Orbiting camera detects reflected light to determine the extent of the planet's vegetation.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome infertile men have heightened cancer risk
Those who don’t make sperm are more likely than fertile men to develop a malignancy.
By Nathan Seppa