All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBaby-led weaning won’t necessarily ward off extra weight
Babies allowed to feed themselves gained similar amounts of weight as babies spoon-fed by caretakers.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsResistance to CRISPR gene drives may arise easily
New tools for pest and disease control could become useless without improvements.
-
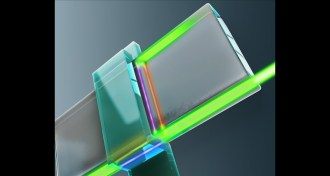 Physics
PhysicsMajorana fermion detected in a quantum layer cake
Scientists found evidence of a particle that is its own antiparticle.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCows produce powerful HIV antibodies
For the first time in any animal, researchers elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV. Cows’ antibodies could help with drug development.
-
 Animals
AnimalsElephant seals recognize rivals by the tempo of their calls
The distinct sputtering-lawnmower sound of a male elephant seal’s call has a tempo that broadcasts his identity to competitors.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNew Horizons’ next target caught making a star blink
The team behind the spacecraft that visited Pluto has seen its next quarry blocking the light from a distant star.
-
 Tech
TechThis robot grows like a plant
A new soft robot navigates its environment by growing in a manner inspired by plants.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThese genes may be why dogs are so friendly
Dog domestication may be the result of just a few genetic changes, including ones that made canines more interested in interacting with people.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHumans first settled in Australia as early as 65,000 years ago
Australia may have said “G’day” to humankind thousands of years earlier than previously believed.
-
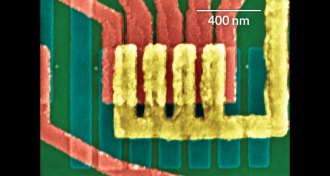 Tech
TechThe incredible shrinking transistor just got smaller
Tiniest transistor, made with carbon nanotubes, suggests computers aren’t done shrinking down.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCommon drugs help reverse signs of fetal alcohol syndrome in rats
A thyroid hormone and a blood sugar drug affect levels of a hormone needed for brain development, study in rats shows.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDog domestication happened just once, ancient DNA study suggests
DNA of ancient canines counters idea that dogs were domesticated twice, in Europe and Asia.