All Stories
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaur tail preserved in amber, with feathers
The tail of a dinosaur trapped in amber includes both feathers and identifiable bits of bone.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
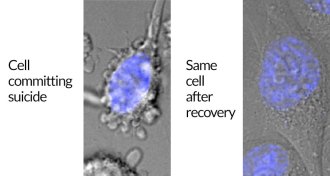
LifeCells avoiding suicide may play role in spread of cancer
A newly discovered process can pull cells back from the brink of death.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsVacuum’s quantum effect on light detected
Light can be polarized through interactions with empty space.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEpigenetic marks may help assess toxic exposure risk — someday
Exposure to things in the environment may change chemical tags on DNA and proteins, but it’s still unclear how to use that data to assess health risks.
-
 Life
LifeEarly RNA may have used isolation strategy to defeat useless mutants
Temporary barriers help RNA escape shorter, faster-replicating parasites
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceGraphene Silly Putty detects pitter-patter of spider footsteps
Sensor made of graphene and Silly Putty can detect pulse, breathing — and spider feet.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHealth official calls on neuroscience to fight mental illness
When it comes to mental health, all countries are developing countries, WHO official says, appealing to neuroscience for help.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOldest traces of smallpox virus found in child mummy
The oldest genetic evidence of smallpox comes from variola virus DNA found in a child mummy buried in a church crypt in Lithuania.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy crested penguins lay mismatched eggs
After long migratory swims, crested penguins lay one small and one larger egg.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
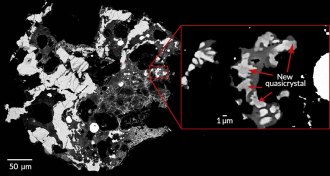
EarthThird kind of quasicrystal found in Russian meteorite
A new quasicrystal found inside a Russian meteorite is the first ever found in nature before being synthesized in the lab.
-
 Life
LifeHaving an extra chromosome has a surprising effect on cancer
Extra chromosome copies may protect against, not cause, cancer.
-
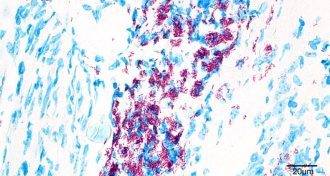 Ecosystems
EcosystemsLosing tropical forest might raise risks of human skin ulcers, deformed bones
Bacteria that cause Buruli ulcer in people flourish with tropical deforestation.
By Susan Milius