All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyKepler tally grows: 104 more exoplanets confirmed
Kepler space telescope adds another 104 planets to its growing census of worlds in our galaxy.
-
 Health & Medicine
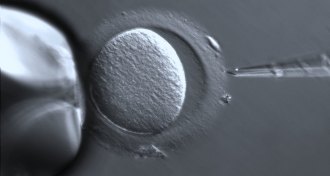
Health & MedicineIVF doesn’t up long-term breast cancer risk, study says
A Dutch study of more than 25,000 women over two decades suggests that IVF-treated women are no more likely to get breast cancer than other women.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHerbicide no match for fruit flies’ gut microbes
Friendly gut bacteria team up to break down herbicide that might otherwise harm fruit flies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNo one-fits-all healthy diet exists
Mice’s response to diet varies with their genes.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists throw a curve at knuckleball explanation
Wildly swerving pitches may be the result of a phenomenon known as a “drag crisis”
-
-
 Science & Society
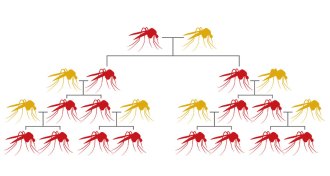
Science & SocietyGM mosquitoes succeed at reducing dengue, company says
GM mosquito releases in Brazil have helped cut dengue cases 91 percent in a year.
By Susan Milius -
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFirst case of woman-to-man spread of Zika via sex reported
The first known case of female-to-male sexual transmission of Zika virus has been reported in New York City.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsFor jaguars, armored prey is no obstacle
With big heads, thick teeth and strong muscles, jaguars have evolved to take on dangerous prey, often animals covered with thick armor.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBlack hole born without stellar parent, evidence suggests
A galaxy in the early universe might harbor the first known “direct collapse” black hole, one that forms when a cloud of gas collapses under its own weight without forming stars.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExercise helps you get in shape for old age
Exercise can fend off the effects of aging on the body and brain.