All Stories
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHippocampus makes maps of social space, too
The hippocampus is a multitalented mapmaker.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDome effect leaves Chinese megacities under thick haze
Airborne black carbon lowers an atmospheric boundary, trapping pollution around major cities and worsening air quality, researchers propose.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceForgetting can be hard work for your brain
It can take more work to forget something than to remember it.
-
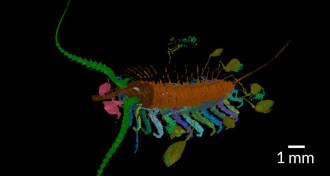 Animals
AnimalsAncient arthropod kept its brood close
A newly discovered ancient arthropod may offer clues on the evolution of parenting styles.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnt antennae provide chemical ID
Ants use their antennae to identify nest-mates and potential invaders. But antennae also produce the key compounds that ants use to tell friend from foe.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnts’ antennae both send and receive chemical signals
Ants use their antennae to identify nest-mates and potential invaders. But antennae also produce the key compounds that ants use to tell friend from foe.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyMarijuana use starting in youth implicated in financial woes
Long-term, heavy pot smoking linked to financial troubles by age 38.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFive things to know about Zika
Last week, a public health poll pointed to some myths that have been circulating about Zika. Let’s bust them.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDisney’s ‘The Jungle Book’ resurrects giant extinct ape
Disney’s latest version of ‘The Jungle Book’ features Gigantopithecus, the largest known ape ever to have lived.
By Erin Wayman -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPossible second Viking site found in Newfoundland
Newfoundland excavation reveals possible Norse settlement.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeNew habitat monitoring tools find hope for tigers
Free tools such Google Earth Engine and Global Forest Watch show there’s still enough forest left for tigers — if it’s protected.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyPulling ‘Vaxxed’ still doesn’t retract vaccine misconceptions
The Tribeca Film Festival’s decision to cancel its screening of an antivaccination film has been lauded as a win for science, but irrationality already won.