News in Brief
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChinese rover reveals moon’s layers
Radar imaging done by China’s Yutu lunar rover reveals that the moon’s geological history could be more complex than once thought.
-
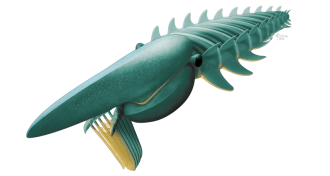 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow arthropods got their legs
New fossils reveal how arthropods evolved branching limbs.
-
 Life
LifeChickens to blame for spread of latest deadly bird flu
Chickens are responsible for the second wave of H7N9 bird flu in China.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeens have higher anaphylaxis risk than younger kids
Adolescents may be more apt to experience an extreme allergic reaction than younger children, researchers report.
By Nathan Seppa -
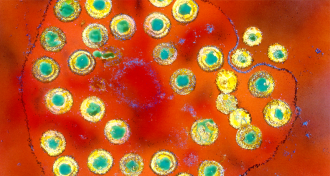 Life
LifeExperimental herpes vaccine works in mice
An experimental herpes vaccine works in animal tests by using an approach starkly different from that used in previous vaccine development.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPossible ancestor of sponges found
An exquisitely preserved 600-million-year-old fossil from China has cell types and a shape resembling sponges, thought to be among the first multicellular animals to evolve.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyRemote star clusters discovered on edge of Milky Way
Two newly discovered star clusters are the first ever seen at the remote edges of the Milky Way.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDose of extra oxygen revs up cancer-fighting immune cells
Extra oxygen helps immune cells shrink tumors in cancer-ridden mice.
-
 Earth
EarthVolcanic lightning forges tiny glass balls from airborne ash
The lightning that crackles through volcanic plumes can melt ash into tiny glass beads.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHundreds of galaxies seen in a new 3-D view of the universe
A new instrument lets astronomers measure the distances to hundreds of galaxies at once, looking back across the age of the universe.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSecondhand smoke exposure in womb linked to eczema in childhood
Secondhand smoke exposure in the womb may heighten risk of eczema and other dermatitis in children, a study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
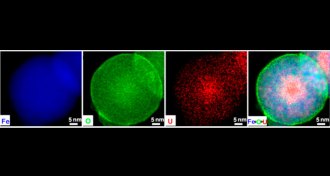 Chemistry
ChemistryIron nanoparticles snatch uranium
With a dash of iron nanoparticles and a magnet, researchers can quickly harvest radioactive fuel.
By Beth Mole