News in Brief
-
 Health & Medicine
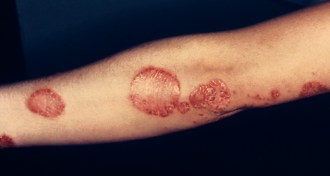
Health & MedicineTwo genes clear up psoriasis and eczema confusion
Psoriasis and eczema are often mistaken for each other, leading to mistreatment. Testing just two genes could eliminate this confusion.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDuck-billed dinosaurs roamed the Arctic in herds
Young and old duck-billed dinosaurs lived together in herds in the Arctic, tracks preserved in Alaska indicate.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomySupernova rapidly creates dust between stars
Astronomers watch a shell of dust form within weeks of a star’s explosion.
-
 Earth
EarthGravity variations foretell flood risk months in advance
Tiny gravitational tugs from saturated river basins allow NASA satellites to forecast flood risk.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFlightless dino-bird wore full-body feathers
Recently unearthed Archaeopteryx fossil sports full coat of feathers, suggesting feather evolution was more complex than previously thought.
-
 Life
LifeStem cell papers retracted
Researchers who reported easy method for making stem cells admit mistakes mar their work, and have retracted their papers from Nature.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBone marrow transplant could reverse sickle cell in adults
A relatively mild treatment involving radiation and chemo followed by a bone marrow transplant may treat sickle cell disease in adults.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Life
LifeOne lichen is actually 126 species and counting
One supposedly well-known tropical lichen could really be several hundred kinds.
By Susan Milius -
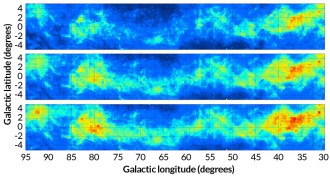 Astronomy
AstronomyMilky Way galaxy’s dust clouds shown in 3-D map
A new three-dimensional map of interstellar dust in the Milky Way wraps 180 degrees around the sky and extends over 16,000 light-years from Earth.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyJust four questions can identify which ER patients need prompt care
A simple decision tree may find serious ailments in ER patients’ fuzzy complaints.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple blood test detects heart transplant rejection
Heart transplant recipients whose bodies are starting to reject the new organ might carry genetic warning signs.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene variant tied to diabetes in Greenlanders
Greenlanders who carry two copies of a newly discovered gene variant have upwards of 10 times the chance of developing type 2 diabetes.