News
-
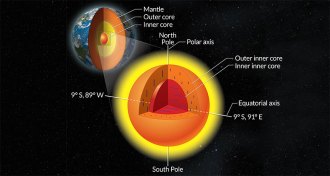 Earth
EarthSolid inner, inner core may be relic of Earth’s earliest days
Earth’s innermost inner core may have formed billions of years earlier than previously thought, shortly after the planet’s accretion.
-
 Climate
ClimateIce rafts traveling farther and faster across the Arctic Ocean
Climate change may be causing Arctic sea ice to travel farther and faster than it did 15 years ago, taking pollutants and other material along for the ride.
-
 Physics
PhysicsGeneral relativity caught in action around black hole
X-rays enable scientists to spot a black hole twisting the surrounding fabric of spacetime, just as Einstein’s theory predicts.
By Andrew Grant -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThigh bone adds to mystery over 14,000-year-old Homo species
Controversial Chinese leg fossil may point to hybrid humans 14,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
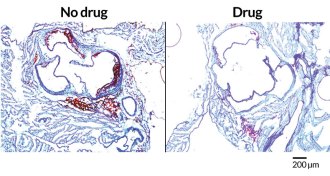 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo treat the heart, start with the gut
Preventing gut bacteria from making certain chemical compounds reduced artery clogging in mice, researchers report.
-
 Life
LifeIn the body, cells move like flocks of birds or schools of fish
Cells move in groups similarly to flocks of birds and schools of fish
-
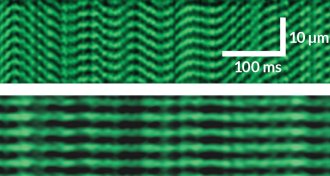 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMini microscope is a window into live muscle tissue
A tiny microscope offers unprecedented views of live human muscles.
-
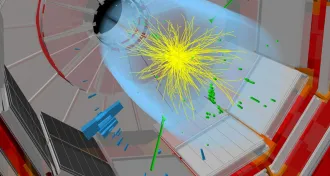 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsLHC restart provides tantalizing hints of a possible new particle
The first comprehensive analyses of the recently restarted Large Hadron Collider yields no clear-cut discoveries but at least one intriguing hint of a new particle.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsForgetful male voles more likely to wander from mate
Poor memory linked to a hormone receptor in the brain could make male prairie voles more promiscuous.
-
 Climate
Climate195 nations approve historic climate accord
The Paris climate talks end with delegates from 195 nations releasing a hard-fought agreement to curb climate change and limit warming to 2 degrees Celsius.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyDebate grows over whether X-rays are a sign of dark matter
The dwarf galaxy Draco, which is chock-full of dark matter, doesn’t emit a band of X-rays that researchers hoped were produced by the mysterious invisible stuff.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeTo push through goo, use itty, bitty propellers
Newly designed micropropellers mimic bacteria to move through viscous surroundings.