News
-
 Animals
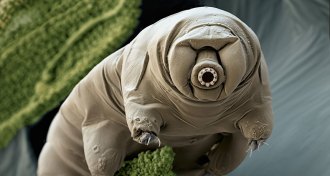
AnimalsWater bears’ genetic borrowing questioned
A new analysis of tardigrade DNA suggests that water bears don’t swap many genes with other organisms after all.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dating of dino ancestor challenges Triassic timeline
New dates for geologic layers of well-known fossil formation show that dinosaurs and their ancient relatives were separated by less time than researchers thought.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA editing shows success in mosquito sterilization
A new gene drive that sterilizes females could reduce numbers of malaria mosquitoes
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHigh-potency pot smokers show brain-fiber damage
People who smoke potent pot had signs of damage in a brain communication link.
-
 Chemistry
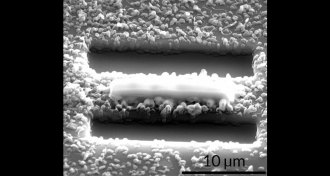
Chemistry‘Q-carbon’ may offer quick route to diamonds
Q-carbon might be the third form of solid carbon, but some scientists have doubts.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Climate
ClimateWarming culprit CO2 has a cool side — and it’s in Antarctica
Rising CO2 levels above central Antarctica cause cooling, not warming, new research suggests. The odd effect results from surface temperatures that are colder than the overlying stratosphere.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHuman gene editing research gets green light
Gene editing research can move forward, but not for reproductive purposes, international summit committee says.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePay attention to that under-the-weather feeling
People can forecast their likelihood of catching colds by rating their own health, study shows.
By Bruce Bower -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsSpooky quantum connection quantified for multiple particles
Physicists have measured quantum entanglement between several particles rather than just two.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsMaxwell’s demon faces the heat
A device inspired by an 1867 thought experiment fails to break the second law of thermodynamics, which governs the flow of heat and the drive toward maximum disorder.
By Andrew Grant -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPeople roamed tip of South America 18,500 years ago
Stone tools, charred animal bones and fire ash found at the Monte Verde site in Chile indicate people reached South America’s southernmost territory at least 18,500 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
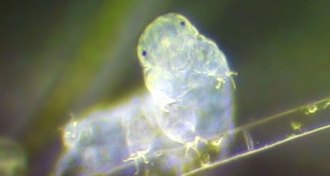
GeneticsWater bears are genetic mash-ups
Drying out may help tardigrades soak up new DNA, which in turn aids the water bears in withstanding stress.