News
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew catalog of human genetic variation could improve diagnosis
Study of human protein-coding variation reveals which genes are more likely to be involved in genetic diseases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChilly cages may skew disease studies in lab mice
Mice studies on diet and human disease might be marred by stress of cold temperatures in their cages.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTwo-stage process formed moon, simulations suggest
Certain elements absent from lunar samples but present on Earth might be hidden deep inside the moon, a relic from how it was put together.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePutting the big chill on cryotherapy
Evidence is lacking for whole-body cryotherapy as a treatment for muscle soreness.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Earth
EarthEarth’s water originated close to home, lava analysis suggests
Scarcity of a hydrogen isotope called deuterium in molten rock from Earth’s depths suggests that the planet’s H2O originated from water-logged dust during formation, not comets.
-
 Computing
ComputingNew algorithm cracks graph problem
A new algorithm efficiently solves the graph isomorphism problem, which has puzzled computer scientists for decades.
By Andrew Grant -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSigns of cardiac disease start early in obese children
Worrisome changes to the heart that are associated with obesity can appear in childhood, a new MRI study shows.
By Laura Beil -
 Astronomy
AstronomyEarly stars found swirling in the Milky Way center
Ancient stars with low iron abundance surround the Milky Way’s center.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHoneybees sweetened early farmers’ lives
Residue on pottery pegs ancient farmers as devotees of honeybee products.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePhobos starting to crack under pressure
Grooves that wrap around Phobos show that the Martian moon is starting to crack from stress.
-

-
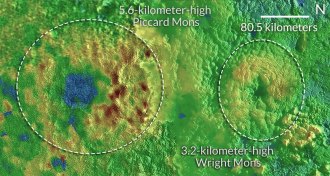 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePluto continues to deliver surprises
Ice volcanoes, young landscapes and twirling moons are just a few more surprises from Pluto.