News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBad kitty: Cat bites can cause nasty infections
Three in 10 patients seeking treatment for hand bites were hospitalized, study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Climate
ClimateStrong winds may have waylaid global warming
Gusts over the Pacific Ocean may have stashed heat underwater since 2001.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateWeather patterns over Southern Hemisphere have a regular pulse
Variations in energy and rainfall over the Southern Hemisphere follow a pattern that repeats every 20 to 30 days.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhen flowers died out in Arctic, so did mammoths
Genetic analysis finds vegetation change in the Arctic around same time as megafauna extinction.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyOld stars gleaned neighbors’ gas, Hubble data show
Blue straggler stars can continue to burn hot after taking material from a stellar companion.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceScientists throw crystals a curve
Particles inside a sphere assemble into ordered ribbons, not lumps.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDiuretic may treat autism, study in rodents suggests
Drug that lowers chloride levels in brain cells staves off symptoms in mice and rats.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFigure skating judges get a 10 for duplicity
Sport’s reform efforts have resulted in more nationalistic bias and vote trading.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVitamin C could give chemo a boost
Injected into mice, the supplement helped anticancer drugs shrink tumors.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsAmazon doesn’t actually go green in dry seasons
An optical illusion in satellite data made forests appear to grow faster.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOvercoming peanut allergy requires maintenance for most
In small study, nearly all people who stopped eating the legumes daily later experienced an allergic reaction.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Particle Physics
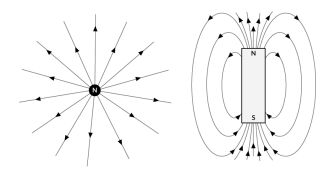
Particle PhysicsSingle-pole magnet emerges in frozen concoction
An experiment has simulated the long-sought magnetic particle.
By Andrew Grant