Uncategorized
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyLasers reveal construction inspired by ancient Mexican pyramids in Maya ruins
Archaeologists have uncovered structures in Guatemala that are remarkably similar to La Ciudadela and its temple at the ancient city of Teotihuacan.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTuskless elephants became common as an evolutionary response to poachers
After poachers tore through a Mozambican elephant population, tuskless females tripled in number as humans altered the species’s evolutionary trajectory.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologySome dinosaurs may have lived in herds as early as 193 million years ago
A fossilized family gathering of long-necked Mussaurus may be the earliest evidence yet of herd behavior in dinosaurs.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyVikings lived in North America by at least the year 1021
Wooden objects provide the most precise dating yet of a Norse settlement in Newfoundland.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists found modern domestic horses’ homeland in southwestern Russia
Two genes tied to endurance and docility may help explain the horses’ success in spreading across Eurasia.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s the physics of why ducklings swim in a row behind their mother
By paddling in just the right spots, ducklings save energy by surfing their mom’s waves, and pass along the benefit to siblings down the line.
-
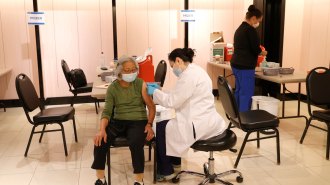 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about booster shots for Moderna’s and J&J’s COVID-19 vaccines
Immunity against the coronavirus is waning, but additional doses of the same or different COVID-19 vaccines could help protect vulnerable people.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAn agile gecko found in India named after the legendary Jackie Chan
A hard-to-catch gecko species is named after martial artist Jackie Chan. Skin patterns, like one resembling a galaxy, inspire other newfound geckos’ names.
-
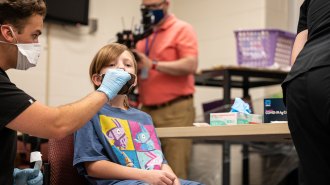 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 testing in schools works. So why aren’t more doing it?
School COVID-19 testing programs can keep kids in class and safe, but face challenges ranging from deciding on a testing strategy to parental buy-in.
-
 Physics
PhysicsAn atomic clock measured how general relativity warps time across a millimeter
A record-breaking result reveals the precision achievable by atomic clocks, letting researchers detect slightly faster ticking over a tiny height change.
-
 Space
Space5 cool things to know about NASA’s Lucy mission to the Trojan asteroids
NASA’s Lucy is the first spacecraft to head to the two giant clumps of space rocks that tag along in Jupiter’s orbit.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBarnacles are famed for not budging. But one species roams its sea turtle hosts
Once settled and glued to the substrate, adult barnacles stay put. But turtle barnacles upend this trend, sliding slowly across their reptilian rides.
By Jake Buehler