Uncategorized
-
 Tech
TechHybrid robot merges flier with two snakelike machines
A helicopter robot can airlift snakelike search-and-rescue bots out of tight situations.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStatins may improve odds of surviving a bleeding stroke
Common cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins may help people who have suffered a stroke caused by ruptured blood vessels.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDyslexic brain may solve some math problems in a roundabout way
Children with dyslexia rely heavily on right brain to do addition problems.
-
 Tech
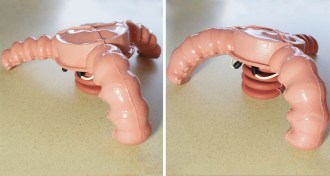
TechHopping robot powered by explosions
A soft-bodied robot that can jump with the help of an explosion could one day aid search-and-rescue operations.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Earth
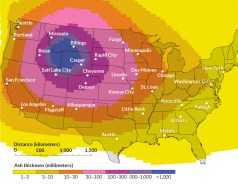
EarthSupervolcano blast would blanket U.S. in ash
A new simulation illustrates the explosiveness of the volcano that lurks beneath Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Fantastic Lab’ recounts battle against typhus, Nazis
Arthur Allen explores how two European scientists produced typhus vaccines during World War II.
-
 Ecosystems
Ecosystems‘Where Do Camels Belong?’ explores invasive species
Ecologist Ken Thompson takes a closer look at the impacts (or lack thereof) of invasive species.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCrops take up drugs from recycled water
Plants irrigated with recycled wastewater can soak up tiny amounts of pharmaceutical compounds but what this means for human health is unclear.
By Beth Mole -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFeedback
Readers discuss sources of stress in everyday life and tell us what they think about NASA's plan to nab an asteroid.
-
 Life
LifeThoughtful approach to antibiotic resistance
Changing how people think about antibiotics is already showing promise in reducing antibiotic use and costs. It’s doubtful, however, that any single strategy will be enough.
By Eva Emerson -
 Paleontology
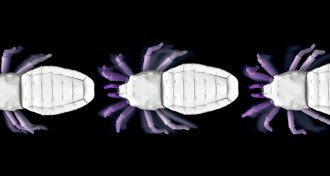
Paleontology3-D scans reveal secrets of extinct creatures
Paleontologists can dig into fossils without destroying them and see what’s inside using 3-D scanning. What they’re learning helps bring the past to life.
-
 Plants
PlantsBorrowed genes raise hopes for fixing “slow and confused” plant enzyme
Inserting some bacterial Rubisco chemistry into a plant might one day boost photosynthesis and help raise crop yields.
By Susan Milius