Uncategorized
-
 Animals
AnimalsFattened livers prep white sharks for extreme migrations
The organ's reserves enable a long journey from waters off California to Hawaii and back, tracking data suggest.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
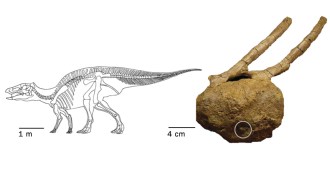
PaleontologyDinosaur had impressive schnoz
Fossils found in Utah reveal geographic segregation of horned species.
By Erin Wayman -
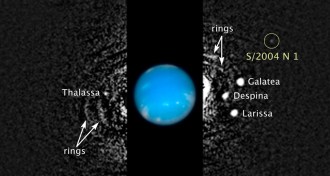 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNeptune gets 14th moon
Images from Hubble Space Telescope reveal tiny, dark satellite orbiting blue-green gas giant.
By Andrew Grant -
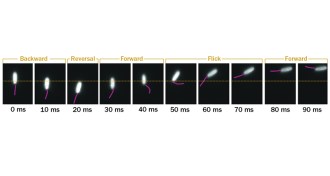
-
 Life
LifeGenetic test fingers viral, bacterial infections
If made to take less time, test could help doctors treat children's fevers.
-
 Tech
TechSound waves put levitation on the move
Technique transports nonmagnetic particles such as cells, water droplets and coffee grounds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyT. rex hunted live prey
Fossils yield tooth in healed wound of another dinosaur.
By Erin Wayman -
 Tech
TechWhat parents just don’t understand about online privacy
Not long ago, police and school officials in Old Saybrook, Conn., held a high school assembly on Internet safety. The purpose of the assembly, wrote New Haven Register reporter Susan Misur, was to make students aware of how public their photos, tweets and profiles are online. To make this point, the presentation included a slide […]
-
 Animals
AnimalsSponges boom thanks to Antarctic ice shelf bust
Previously thought to grow at a slow pace, the sea creatures exploded in number.
-
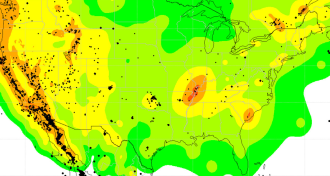 Earth
EarthHuge quakes may foretell smaller, human-caused ones
Distant powerful temblors triggered ominous activity at wastewater injection sites.
By Erin Wayman -
 Genetics
GeneticsKiller whales are (at least) two species
Orca genetics highlights distinctions among groups that feed on different prey.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePermanent Present Tense
The Unforgettable Life of the Amnesic Patient, H. M. by Suzanne Corkin.
By Susan Gaidos