
Laura Sanders reports on neuroscience for Science News. She wrote Growth Curve, a blog about the science of raising kids, from 2013 to 2019 and continues to write about child development and parenting from time to time. She earned her Ph.D. in molecular biology from the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, where she studied the nerve cells that compel a fruit fly to perform a dazzling mating dance. Convinced that she was missing some exciting science somewhere, Laura turned her eye toward writing about brains in all shapes and forms. She holds undergraduate degrees in creative writing and biology from Vanderbilt University in Nashville, where she was a National Merit Scholar. Growth Curve, her 2012 series on consciousness and her 2013 article on the dearth of psychiatric drugs have received awards recognizing editorial excellence.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Laura Sanders
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat do we mean by ‘COVID-19 changes your brain’?
The events of our lives are reflected in the size, shape and behavior of our constantly changing brains. The effects of COVID-19 changes aren’t clear.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow a scientist-artist transformed our view of the brain
The book ‘The Brain in Search of Itself’ chronicles the life of Santiago Ramón y Cajal, who discovered that the brain is made up of discrete cells.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA hit of dopamine sends mice into dreamland
New results are some of the first to show a trigger for the mysterious shifts between REM and non-REM sleep in mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA faulty immune response may be behind lingering brain trouble after COVID-19
The immune system’s response to even mild cases of COVID-19 can affect the brain, preliminary studies suggest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOmicron forces us to rethink COVID-19 testing and treatments
At-home rapid tests may miss the speedy variant early on, and some treatments, such as some monoclonal antibodies, no longer work.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese are the viruses that mRNA vaccines may take on next
Now that mRNA vaccines have proved effective against the coronavirus, scientists are taking aim at influenza, HIV and other viruses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow sleep may boost creativity
In a lab experiment, people who had fallen into a shallow sleep were more likely than non- or deep sleepers to later discover a sly math trick.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny living machines called xenobots can create copies of themselves
When clusters of frog cells known as xenobots form a Pac-Man shape, they are especially efficient at replicating in a new way, researchers say.
-

Can psychedelics meet their potential for treating mental health disorders?
Psychedelics hold lots of promise as treatments for mental health disorders like PTSD and depression. But the drugs still face hurdles.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrainless sponges contain early echoes of a nervous system
Simple sponges contain cells that appear to send signals to digestive chambers, a communication system that offer hints about how brains evolved.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA custom brain implant lifted a woman’s severe depression
An experimental device interrupts brain activity linked to a woman’s low mood. The technology, she said, has changed her lens on life.
-
 Health & Medicine
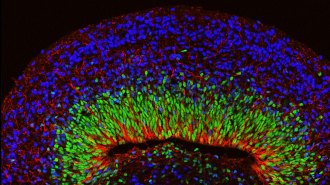
Health & MedicineHow personalized brain organoids could help us demystify disorders
Personalized clusters of brain cells made from people with Rett syndrome had abnormal activity, showing potential for studying how human brains go awry.