Video
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
Life‘PigeonBot’ is the first robot that can bend its wings like a real bird
Insights into the joint movements and feather surface structures that help birds control their wing shape could help robotic flyers move more deftly.
-
 Life
LifeFluid dynamics may help drones capture a dolphin’s breath in midair
High-speed footage of dolphin spray reveals that droplets blast upward at speeds approaching 100 kilometers per hour.
-
 Life
LifeStick-toting puffins offer the first evidence of tool use in seabirds
Puffins join the ranks of tool-using birds after researchers document two birds using sticks to groom, a first for seabirds.
-
 Life
LifeKoalas aren’t primates, but they move like monkeys in trees
With double thumbs and a monkey-sized body, an iconic marsupial climbs like a primate.
By Susan Milius -
 Space
Space2019 brought us the first image of a black hole. A movie may be next
The Event Horizon Telescope team is gearing up for more black hole discoveries.
-
 Climate
ClimateSee how an Alaskan glacier has shrunk over time
Scientists have created a time-lapse series of images of the retreat of an Alaskan glacier using NASA and U.S. Geological Survey Landsat data.
-
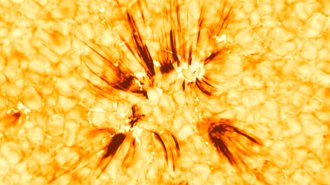 Space
SpaceRealigning magnetic fields may drive the sun’s spiky plasma tendrils
Solar spicules emerge near counterpointing magnetic fields, hinting that self-adjusting magnetism creates these filaments, which may heat the corona.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFlipping a molecular switch can turn warrior ants into foragers
Toggling one protein soon after hatching makes Florida carpenter ants turn from fighting to hunting for food.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsSilver-backed chevrotains have been ‘rediscovered’ by science after 29 years
With help from Vietnamese villagers, researchers captured photos of a species of deerlike ungulate thought lost to science nearly three decades ago.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep may trigger rhythmic power washing in the brain
Strong, rhythmic waves of cerebrospinal fluid wash into the human brain during sleep and may help clean out harmful proteins.
-
 Life
LifeVampire bat friendships endure from captivity to the wild
Vampire bats can form social bonds that persist from a lab setting to the outdoors, suggesting the cooperative relationships are like friendships.
-
 Life
LifeSaharan silver ants are the world’s fastest despite relatively short legs
Saharan silver ants can hit speeds of 108 times their body length per second.
By Susan Milius