Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateA carbon footprint life cycle assessment can cut down on greenwashing
As companies try to reduce their carbon footprint, many are doing life cycle assessments to quantify the full carbon cost of their products.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCommon, cheap ingredients can break down some ‘forever chemicals’
Forever chemicals, or PFAS, are harmful compounds that are very difficult to degrade. But some are no match for lye and dimethyl sulfoxide.
By Jude Coleman -
 Chemistry
ChemistryThese researchers are unlocking Renaissance beauty secrets
An art historian has teamed up with chemists to uncover the science behind cosmetics used around 500 years ago.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCats chewing on catnip boosts the plant’s insect-repelling powers
When cats tear up catnip, it increases the amount of insect-repelling chemicals released by the plants.
By Anil Oza -
 Chemistry
ChemistryA pigment’s shift in chemistry robbed a painted yellow rose of its brilliance
The degradation of an arsenic-based paint stripped shadows and light from a still life flower in a 17th century work by painter Abraham Mignon.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsJust 3 ingredients can quickly destroy widely used PFAS ‘forever chemicals’
Ultraviolet light, sulfite and iodide break down enduring PFAS molecules faster and more thoroughly than other UV-based methods.
By Nikk Ogasa -
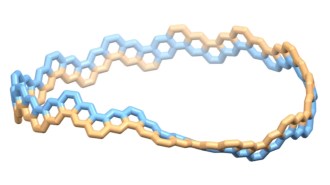 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists made a Möbius strip out of a tiny carbon nanobelt
A twisted belt of carbon atoms joins carbon nanotubes and buckyballs in the list of carbon structures scientists can create.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureOat and soy milks are planet friendly, but not as nutritious as cow milk
Plant-based milks are better for the environment, but nutrition-wise they fall behind cow milk.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Chemistry
ChemistryGrainy ice cream is unpleasant. Plant-based nanocrystals might help
The growth of large ice crystals in ice cream produces a coarse texture. A cellulose nanocrystal stabilizer could help keep the unwelcome iciness away.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Climate
ClimateSmoke from Australia’s intense fires in 2019 and 2020 damaged the ozone layer
Massive fires like those that raged in Australia in 2019–2020 can eat away at Earth’s protective ozone layer, researchers find.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryMarie Maynard Daly was a trailblazing biochemist, but her full story may be lost
Marie Maynard Daly was the first African American woman to receive a Ph.D. in chemistry, but her own perspective on her research is missing from the historical record.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryOne forensic scientist is scraping bones for clues to time of death
The bones of more than 100 cadavers are shedding light on a more precise and reliable way to determine when someone died.