Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA popular heartburn medicine doesn’t work as a COVID-19 antiviral
In lab tests, an antacid didn’t prevent coronavirus infection, but clinical tests are needed to see if it can help people who already have COVID-19.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient DNA suggests Vikings may have been plagued by smallpox
Viral genetic material from human remains provides direct evidence that smallpox infected people dating back to the year 603.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMasks help new moms with COVID-19 safely breastfeed their babies
A study reports newborns could be held and breastfed safely when moms with COVID-19 wore masks and cleaned their hands.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo prevent the next pandemic, we might need to cut down fewer trees
Investing in halting deforestation and limiting the wildlife trade could be a cost-effective way to reduce the risk of pandemics, a new analysis finds.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStone artifacts hint that humans reached the Americas surprisingly early
Finds uncovered in a Mexican cave suggest North America may have had human inhabitants more than 30,000 years ago — way before archaeologists thought.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA blood test may show which COVID-19 patients steroids will help — or harm
An inflammation marker was a good indicator of which patients had lower or higher risks of dying or needing a ventilator when given steroids.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 vaccines by Oxford, CanSino and Pfizer all trigger immune responses
In three clinical trials, vaccine candidates appear safe and induce the production of antibodies and other immune cell responses against the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
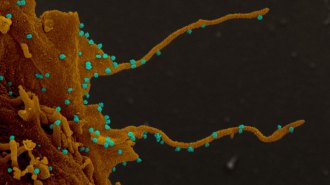
Health & MedicineCoronavirus-infected cells sprout filaments that may spread the virus
Like other coronaviruses, the virus behind COVID-19 causes infected cells to grow spindly projections that may act as highways to other cells.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Space
SpaceWhat will astronauts need to survive the dangerous journey to Mars?
Going to Mars, astronauts will need protections from microgravity and radiation, plus miniature medical devices to diagnose problems and help handle emergencies.
-
 Humans
HumansCompetitive hot dog eaters may be nearing humans’ max eating speed
Just how many hot dogs can one human eat in 10 minutes? New research suggests the answer is 83.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRemdesivir may work even better against COVID-19 than we thought
Gilead Sciences says remdesivir cuts the chances of dying from the coronavirus, and data show the drug can curb the virus’s growth in cells and mice.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThis 1.4-million-year-old hand ax adds to Homo erectus’ known toolkit
A newly described East African find, among the oldest bone tools found, shows the ancient hominids crafted a range of simple and more complex tools.
By Bruce Bower