Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMemory manipulation is the stuff of sci-fi. Someday it could be real
Experiments point to how scientists can strengthen or weaken memories, which may eventually lead to treatments for Alzheimer’s disease or PTSD.
-
 Climate
ClimateA lush, green Arabian Desert may have once linked Africa and Asia
Mineral formations in caves reveal recurring periods of humidity in the Arabian Desert over the last 8 million years.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStone Age hunter-gatherers may have been surprisingly skilled seafarers
New archaeological finds in Malta add to an emerging theory that early Stone Age humans cruised the open seas.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRare books covered with seal skin hint at a medieval trade network
The furry seal skins may have made their way to French monasteries from as far away as Greenland.
By Alex Viveros -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe U.S. measles outbreak shows no signs of slowing
As a second Texas child dies from the preventable disease, HHS Secretary Kennedy is now urging measles vaccination yet still touting unproven treatments.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Arabian cymbals ring up Bronze Age musical connections
Copper instruments discovered at a 4,000-year-old site in Oman echo ritual influences from South Asia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow U.S. public health cuts could raise risks of infectious diseases
Deep funding cuts and widespread layoffs impact everything from local public health outreach to global disease surveillance, making us more vulnerable, experts warn.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA shingles vaccine may also help reduce dementia risk
Analysis of a Welsh program offering live-attenuated shingles vaccines to people born after a certain date showed a 20 percent relative drop in dementia risk.
By Alex Viveros -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSkin cells emit slow electric pulses after injury
The electric skin cell signals, which move at glacial pace compared to those in nerve cells, may play a role in initiating healing.
-
 Health & Medicine
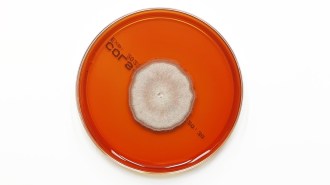
Health & MedicineA new antifungal drug works in a surprising way
Mandimycin, which targets a different essential fungi cell resource than other antifungal drugs, should harm other cell types as collateral — but doesn’t.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertal-like tools found in China present a mystery
A style of primitive stone tools named for the French site where they were first discovered have shown up half a world away.
By Bruce Bower -
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceAI is helping scientists decode previously inscrutable proteins
A new set of artificial intelligence models could make protein sequencing even more powerful for better understanding cell biology and diseases.