Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
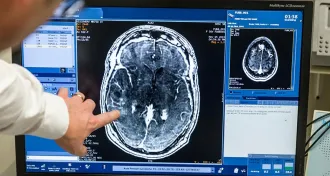
Health & MedicineSigns of cardiac disease start early in obese children
Worrisome changes to the heart that are associated with obesity can appear in childhood, a new MRI study shows.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood-brain barrier jiggled loose to deliver medicine
Using ultrasounds, doctors attempted to slip a chemotherapy drug into a woman’s brain through the blood-brain barrier.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood-brain barrier jiggled loose to deliver medicine
Using ultrasounds, doctors attempted to slip a chemotherapy drug into a woman’s brain through the blood-brain barrier.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCardiac risks rise for linemen during football season
Linemen on a football team face raised cardiac risk over the course of a season, a study of college players shows.
By Laura Beil -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHoneybees sweetened early farmers’ lives
Residue on pottery pegs ancient farmers as devotees of honeybee products.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
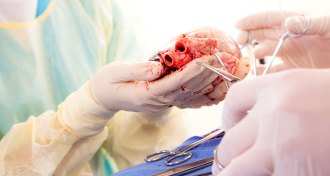
Health & MedicineOrgan waiting list policy benefits the wealthy, study charges
Wealthier patients can afford to get on more organ transplant lists, giving them an advantage, a new study says.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple steps can offer health benefits
Studies find that even small changes in eating habits and movement can lower risk of heart disease.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
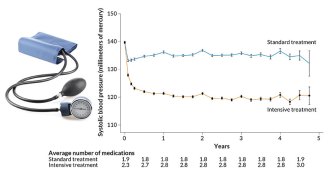
Health & MedicineDropping blood pressure to 120 lowers heart woes, data confirm
Aggressive treatment to lower systolic blood pressure to 120 reduces risk of heart attack, but causes some side effects.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies to fight Alzheimer’s may have unexpected consequences
Alzheimer’s-targeted antibodies make neurons misbehave even more, a study of mice shows.
-
 Life
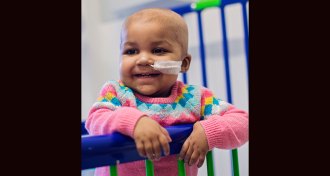
LifeGene editing helps a baby battle cancer
Doctors used molecular scalpels to tweak T cells to target leukemia but not harm the patient.
-
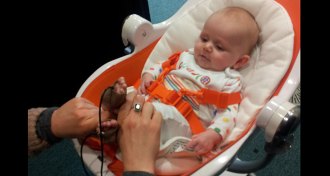 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung babies live in a world unto themselves
Young babies don’t let information from the outside throw off their touch perception, a finding that has clues for how babies experience the world.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominids used wooden spears to fend off big cats
Saber-toothed cat remains suggest ancient hominids used wooden spears as defensive weapons.
By Bruce Bower