Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen selenium is scarce, brain battles testes for it
In competition for selenium, testes draw the nutrient away from the brain.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyCaffeine gives cocaine an addictive boost
Not only is it popular to “cut” cocaine with caffeine, the combination might be more addictive.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
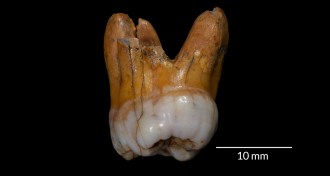 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsNew catalog of human genetic variation could improve diagnosis
Study of human protein-coding variation reveals which genes are more likely to be involved in genetic diseases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChilly cages may skew disease studies in lab mice
Mice studies on diet and human disease might be marred by stress of cold temperatures in their cages.
-
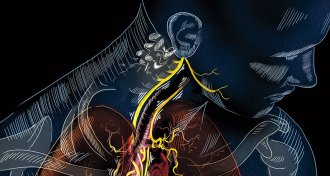 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceViva vagus: Wandering nerve could lead to range of therapies
Researchers are testing ways to stimulate the vagus nerve to treat a slew of ailments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePutting the big chill on cryotherapy
Evidence is lacking for whole-body cryotherapy as a treatment for muscle soreness.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMummified boy’s DNA unveils new but ancient maternal lineage
An Inca child’s DNA shows he hailed from a newly identified line of maternal ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSigns of cardiac disease start early in obese children
Worrisome changes to the heart that are associated with obesity can appear in childhood, a new MRI study shows.
By Laura Beil