Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentLatest BPA replacement seeps into people’s blood and urine
Replacements for BPA called BPS and BPSIP may raise health risks for cashiers.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith flibanserin approval, a complicated drug takes the spotlight
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first drug to increase women’s sexual desire. But whether the benefits outweigh the side effects depends on who you ask.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow farm life can prevent allergies
Farm dust prevents allergies by turning on an anti-inflammatory enzyme in the cells lining mice’s lungs.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhy enforced ‘service with a smile’ should be banned
If management wants workers to maintain false cheer, those workers should be trained, supported and compensated for the emotional labor, a new review suggests.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient pottery maps route to South Pacific
New Guinea pottery points to a key meeting of island natives and seafarers at least 3,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMicrobes make the meal, new diet book proposes
Researcher Tim Spector skewers conventional thinking about weight loss in ‘The Diet Myth’
By Meghan Rosen -
 Materials Science
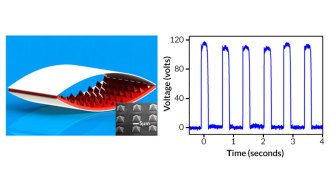
Materials ScienceNanogenerators harvest body’s energy to power devices
Nanogenerators offer body-harvested energy to fuel bionic future
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe need to feed and eating for pleasure are inextricably linked
Scientists used to think that the hunger and the pleasure from food could be easily distinguished. But new results show these systems are inextricably intertwined.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaccinated man excretes live poliovirus for nearly 3 decades
For almost 30 years, a man with an immune deficiency has been shedding poliovirus strains that have evolved from the version he received in a vaccine.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPsychology results evaporate upon further review
Less than half of psychology findings get reproduced on second tries, a study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarlier is better for HIV treatment
People infected with HIV benefit from starting a drug regimen early, an international study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Humans
HumansMoon bounces, bad spider leaders and more reader feedback
Readers debate faith's role in evolution, compare politicians to spiders and more.