Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Environment
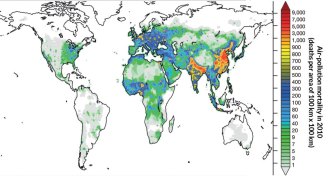
EnvironmentHome fires, farm fumes are leading causes of air-pollution deaths
Deadly air pollution comes from surprising sources, but toxicity of different types is still up in the air.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBackwash from nursing babies may trigger infection fighters
A nursing baby’s saliva may get slurped back into mom’s breast, where it stimulates an immune response.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople find the skin of others’ softer than their own
Humans perceive other peoples’ skin as softer and smoother than their own because touch is important in social bonding, researchers suggest.
-
 Archaeology
Archaeology‘Superhenge’ once lined Stonehenge neighborhood
A row of massive, now-buried stones once bordered a site near Stonehenge.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClinical trial suggests new blood pressure standard
Preliminary results from a clinical trial suggest lower blood pressure targets could reduce rates of cardiovascular diseasae.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePlant spills crucial details for making cancer drug
By injuring the Himalayan mayapple, researchers worked out how the plant makes an important ingredient in a common cancer drug.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLess vitamin D and melatonin bad for multiple sclerosis
Vitamin D and melatonin play important roles in multiple sclerosis.
-
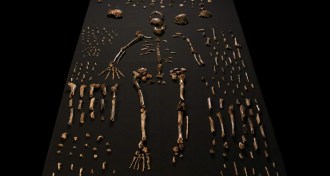 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossils suggest new species from human genus
Undated South African cave fossils may reveal a new species in the human genus.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyImmortality and more in reader feedback
This week in reader feedback: Immortality and tracing ancient humans.
-
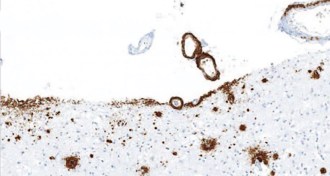 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMisfolded proteins implicated in more brain diseases
Alzheimer’s, other disorders show similarity to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other prion infections.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMinutes after encountering danger, lemurs yawn
Madagascar primates yawn within minutes of encountering threats.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsA monkey uses a stick to pick its teeth and nose
A wild bearded capuchin monkey in Brazil was caught using tools to pick its nose and teeth.
By Erin Wayman