Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyBronze Age mummies identified in Britain
Bone analysis finds widespread mummy making in ancient England and Scotland.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeBabies low on key gut bacteria at higher risk of asthma
Asthma risk may be set early in life, but mice data suggest that the risk could altered by friendly gut bacteria.
-
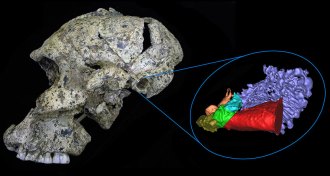 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominid ears were tuned to high frequencies
Two ancient hominid species may have heard high-frequency sounds especially well.
By Bruce Bower -
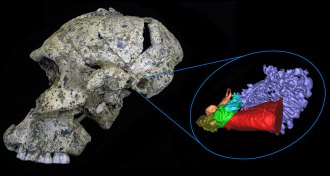 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominid ears were tuned to high frequencies
Two ancient hominid species may have heard high-frequency sounds especially well.
By Bruce Bower -
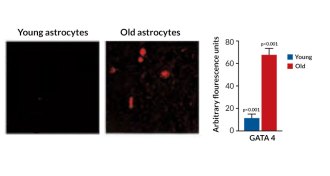 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat makes cells stop dividing and growing
Scientists have found that the protein GATA4 helps control cellular senescence, and may be a target for treating aging-related diseases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving sex doesn’t trigger heart attacks, study suggests
Sex doesn’t trigger heart attacks, study of patients with cardiovascular disease suggests.
By Meghan Rosen -
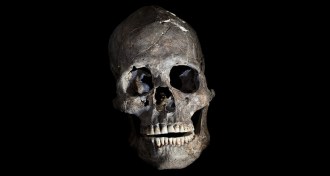 Anthropology
AnthropologyMore than 9,000-year-old decapitated head discovered in Brazil
Human decapitation goes back more than 9,000 years in the Americas.
By Bruce Bower -
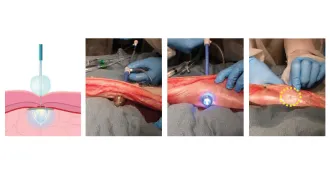 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBalloons-and-glue device seals remote wounds inside the body
To repair damaged tissue, surgeons can deliver a glue patch using two balloons and a blast of UV light.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCoffee serves up surprising health benefits
Reporting on the current state of research allows readers to see beyond the single, sometimes conflicting public health messages that medical studies produce.
By Eva Emerson -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHanded-down tales tell of ancient sea level rise
Australian Aborigines tell tales of actual, ancient sea-level rises, a contested study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIsaac Kinde: Finding cancer via altered genes
Isaac Kinde helped create a technology that can spot cancers early to give patients a better chance at survival.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor kids learning new words, it’s all about context
By recording the first three years of life, researchers get hints about a child’s language development.