Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
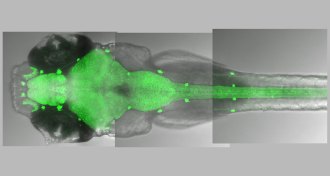
NeuroscienceBoth fish and humans have REM-like sleep
Sleeping zebrafish have brain and body activity similar to snoozing mammals, suggesting that sleep evolved at least 450 million years ago.
-
 Oceans
OceansA mysterious coral disease is ravaging Caribbean reefs
Scientists are racing to learn what’s behind a disease that’s “annihilating” whole coral species in hopes of stopping it.
-
 Neuroscience
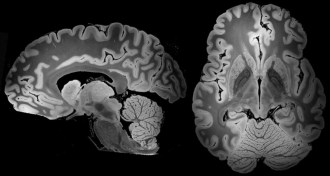
NeuroscienceA 100-hour MRI scan captured the most detailed look yet at a whole human brain
Researchers report ultraprecise imaging of a postmortem human brain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGround beetle genitals have the genetic ability to get strange. They don’t
A new look at the genetics of sex organs finds underpinnings of conflicts over genital size.
By Susan Milius -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsMoonlight shapes how some animals move, grow and even sing
The moon’s light influences lion prey behavior, dung beetle navigation, fish growth, mass migrations and birdsong.
By Erin Wayman -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceReaders wanted to know about asteroids, lithium batteries and more
Readers had questions and comments about asteroids, lithium batteries, and pyroclastic flows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBreaking down the science behind some of your favorite summer activities
Inject some science into your summer.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA reveals the origins of the Philistines
A mysterious Biblical-era population may have fled Bronze Age calamities.
By Bruce Bower -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsWhy some insect eggs are spherical while others look like hot dogs
Analyzing a new database of insect eggs’ sizes and shapes suggests that where eggs are laid helps explain some of their diversity of forms.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Health & Medicine
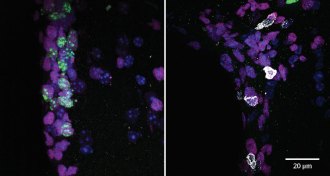
Health & MedicineRogue immune cells can infiltrate old brains
Killer T cells get into older brains where they may make mischief, a study in mice and postmortem human brain tissue finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThis brain region may be why some robots send chills down your spine
Scientists may have traced the source of the “uncanny valley” sensation in the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVision cells can pull double duty in the brain, detecting both color and shape
Neurons in a brain area that handles vision fire in response to more than one aspect of an object, countering earlier ideas, a study in monkeys finds.