Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new study challenges the idea that the placenta has a microbiome
A large study of more than 500 women finds little evidence of microbes in the placenta, contrary to previous reports on the placental microbiome.
-
 Paleontology
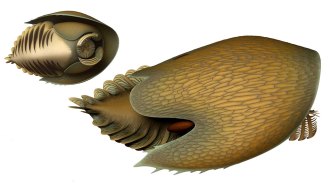
PaleontologyThis newfound predator may have terrorized the Cambrian seafloor
A newly discovered spaceship-shaped predator raked through the Cambrian seafloor in search of food.
-
 Life
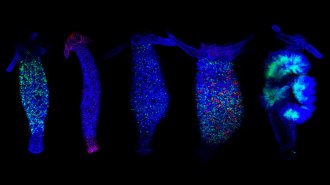
LifeMapping how the ‘immortal’ hydra regrows cells may demystify regeneration
In the continually regenerating hydra, fluorescent markers help researchers track stem cells on the way to their cellular fate.
-
 Life
LifeGiving cats food with an antibody may help people with cat allergies
Research by pet-food maker Purina aims to disable the major allergen carried in cat saliva, a protein called Fel d1.
-
 Life
LifeImmune system defects seem to contribute to obesity in mice
Subtle defects affecting T cells altered the animals’ microbiome and fat absorption, providing hints of what might also be going on in people.
-
 Life
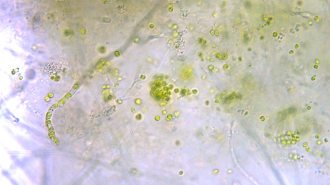
LifeThis is the first fungus known to host complex algae inside its cells
In the lab, an alga and a fungus teamed up to exchange food, similar to lichens. But instead of staying outside, the alga moved into the fungal cells.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA frog study may point to where parenting begins in the brain
Two brain regions, including one active in mammal parents, lit up with activity in both male and female poison frogs when caring for their tadpoles.
-
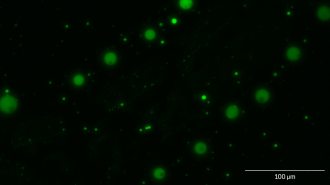 Chemistry
ChemistryDroplets of these simple molecules may have helped kick-start life on Earth
Simple molecules called alpha hydroxy acids form cell-sized structures in conditions mimicking early Earth chemistry.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBoosting a gut bacterium helps mice fight an ALS-like disease
Gut bacteria may alter ALS symptoms for good or ill.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA flexible bone that helps mammals chew dates back to the Jurassic Period
A flexible bone that helps with chewing may have helped give rise to the Age of Mammals, a new fossil shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineManipulating nerve cells makes mice ‘see’ something that’s not there
Using optogenetics to stimulate about 20 nerve cells causes mice to perceive nonexistent vertical or horizontal lines.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA deadly fungus gives ‘zombie’ ants a case of lockjaw
Clues left on infected ant jaws may reveal how the ‘zombie-ant-fungus’ contracts ant muscles to make their death grip.