Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese spiders may have the world’s fastest body clocks
Three orb-weaving spiders may have the shortest circadian clocks yet discovered among animals.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe Lord Howe stick insect is officially back from the dead
New genomic sequencing confirms that stick insects discovered near Lord Howe Island are the assumed-extinct Lord Howe stick insect.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient European farmers and foragers hooked up big time
Interbreeding escalated in regionally distinct ways across Neolithic Europe.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsThis deep-sea fish uses weird eyes to see in dark and light
The eyes of deep-sea fish called pearlsides contain cells that look like rods but act like cones.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCrested pigeons sound the alarm with their wings
Crested pigeons have specialized feathers that signal danger when they flee from an apparent threat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHoneybees fumble their way to blueberry pollination
Blueberry flowers drive honeybees to grappling, even stomping a leg or two down a bloom throat, to reach pollen.
By Susan Milius -
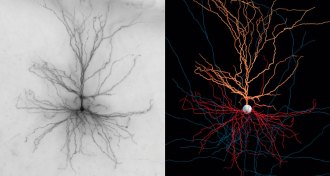 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSee these first-of-a-kind views of living human nerve cells
A catalog of live brain cells reveals stunning diversity and intricate shapes, and may help scientists understand the abilities of the human brain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEPA OKs first living pest-control mosquito for use in United States
Feds approve non-GM male tiger mosquitoes for sale as fake dads to suppress local pests.
By Susan Milius -
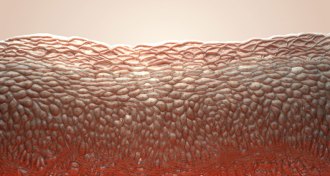 Genetics
GeneticsScientists replaced 80 percent of a ‘butterfly’ boy’s skin
By correcting genes in stem cells and growing new skin in the lab, a new therapy repaired a genetic skin disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman study supports theory on why dengue can be worse the next time around
The amount of dengue antibodies leftover in the blood may up the chances of a severe second dengue infection, a study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFace it: Sheep are just like us when it comes to recognizing people
Sheep trained to recognize celebrity faces demonstrate that the animals have face-recognition capabilities similar to humans and other primates.
-
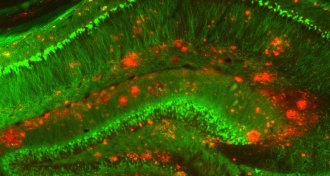 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s protein can travel from blood to build up in the brain
Experiments in mice show Alzheimer’s protein can travel from the blood of an affected mouse to the brain of a healthy animal.