Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSurgeon aims to diagnose deformities of extinct saber-toothed cats
Using CT scans, one orthopedic surgeon is on a quest to diagnose deformities in long-dead saber-toothed cats.
-
 Climate
ClimateDuring El Niño, the tropics emit more carbon dioxide
El Niño increases carbon emissions from the tropics — mimicking future climate change.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThere’s no rest for the brain’s mapmakers
Navigational grid cells stay on the job during sleep.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWe’re more Neandertal than we thought
Neandertals contributed more to human traits than previously thought.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew deep-sea sponge could play a starring role in monitoring ocean health
A new species of sponge that dwells on metal-rich rocks could help scientists track the environmental impact of deep-sea mining.
-
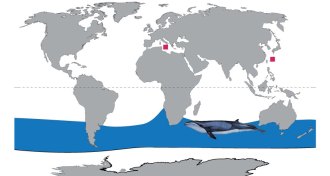 Animals
AnimalsAncient whale turns up on wrong side of the world
A Southern Hemisphere whale species was briefly a northern resident.
-
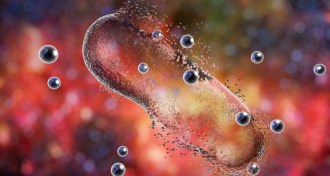 Tech
TechSuperbugs may meet their match in these nanoparticles
Quantum dots and antibiotics hit bacteria with a one-two punch.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNew book offers a peek into the mind of Oliver Sacks
The wide-ranging essays in Oliver Sacks’ ‘The River of Consciousness’ contemplate evolution, memory and more.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureMuch of the world’s honey now contains bee-harming pesticides
A controversial group of chemicals called neonicotinoids has a global impact, tests of honey samples show.
-
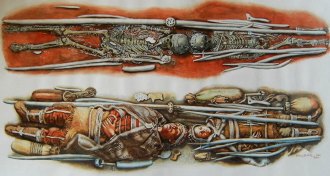 Genetics
GeneticsAncient humans avoided inbreeding by networking
Ancient DNA expands foragers’ social, mating networks.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsJosé Dinneny rethinks how plants hunt for water
Plant biologist José Dinneny probes the very beginnings of root development, which may have important implications for growing food in a changing climate.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeKC Huang probes basic questions of bacterial life
A physicist by training, Kerwyn Casey Huang tries to understand cell shape, movement and growth.