Materials Science
-
 Materials Science
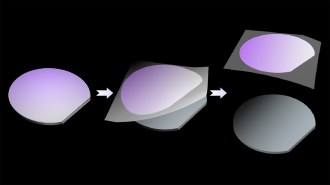
Materials ScienceScotch tape is key to creating thin films of diamond
The sticky stuff helped peel sheets of diamond less than a micrometer thick off silicon wafers, creating membranes useful for electronic devices.
-
 Materials Science
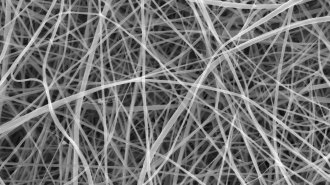
Materials ScienceStarchy nanofibers shatter the record for world’s thinnest pasta
The fibers, made from white flour and formic acid, average just 372 nanometers in diameter and might find use in biodegradable bandages.
By Skyler Ware -
 Health & Medicine
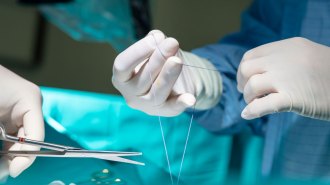
Health & MedicineNew electrical stitches use muscle movement to speed up healing
In rats, the sutures hastened recovery and reduced the risk of infection.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA materials scientist seeks to extract lithium from untapped sources
Lithium is an essential ingredient for batteries in electric vehicles but getting enough will become a problem.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, some of plastic’s toxic hazards were exposed
Worker exposure to vinyl chloride became tightly regulated after the chemical was linked with liver cancer. Now, its use may be on the chopping block.
-
 Climate
ClimateZigzag walls could help buildings beat the heat
A corrugated exterior wall reflects heat to space and absorbs less heat from the ground, keeping it several degrees cooler than a flat wall.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceJurassic Park’s amber-preserved dino DNA is now inspiring a way to store data
DNA is capable of encoding all sorts of data. Storing it in an amberlike material may keep that information safe for nearly forever.
By Payal Dhar -
 Materials Science
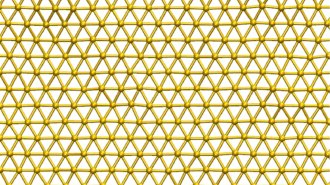
Materials ScienceScientists developed a sheet of gold that’s just one atom thick
Ultrathin goldene sheets could reduce the amount of gold needed for electronics and certain chemical reactions.
By Skyler Ware -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceArtificial intelligence helped scientists create a new type of battery
It took just 80 hours, rather than decades, to identify a potential new solid electrolyte using a combination of supercomputing and AI.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA fiber inspired by polar bears traps heat as well as down feathers do
Scientists took a cue from polar bear fur to turn an ultralight insulating material into knittable thread.
By Jude Coleman -
 Plants
PlantsSalty sweat helps one desert plant stay hydrated
The Athel tamarisk excretes excess salt through its leaves. The buildup of salt crystals pulls water directly from the air, a study reports.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemists turned plastic waste into tiny bars of soap
Researchers developed a process to turn plastic waste into surfactants, the key ingredients in dozens of products, including soap.