Microbes
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThis plastic-gobbling enzyme just got an upgrade
Scientists tweaked a bacterial enzyme and made it more efficient in breaking down plastics found in polyester and plastic bottles.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new plastic film glows to flag food contaminated with dangerous microbes
Plastic patches that glow when they touch some types of bacteria could be built into food packaging to reduce the spread of foodborne illness.
-
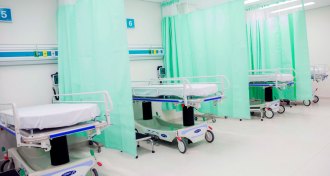 Microbes
MicrobesThis material uses energy from ambient light to kill hospital superbugs
A quantum dot–powered material could help reduce the number of hospital-acquired infections, including those with drug-resistant bacteria.
-
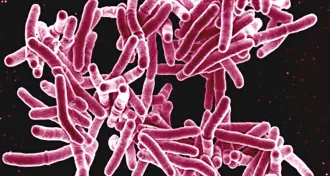 Microbes
MicrobesA new way to make bacteria glow could simplify TB screening
A new dye to stain tuberculosis bacteria in coughed-up mucus and saliva could expedite TB diagnoses and drug-resistance tests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes could record forensic clues to time of death
Scientists have found predictable patterns in the way our genetic machinery winds down after death.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s why so many saiga antelope mysteriously died in 2015
Higher than normal temperatures turned normally benign bacteria lethal, killing hundreds of thousands of the saiga antelopes.
-
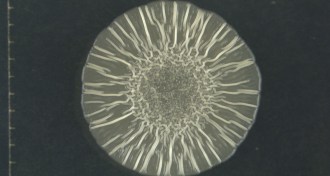 Microbes
MicrobesThe secret to icky, sticky bacterial biofilms lies in the microbes’ cellulose
Bacteria use a modified form of cellulose to form sticky networks that can coat various surfaces.
-
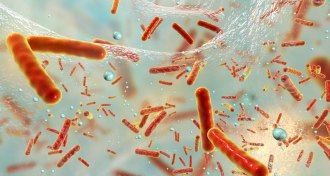 Microbes
MicrobesA new gel could help in the fight against deadly, drug-resistant superbugs
An antibacterial ointment breaks down the defenses of drug-resistant microbes such as MRSA in lab tests.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesNew pill tracks gases through your gut
Swallowing these pill-sized sensors could give new insight into what’s going on in your gut.
-
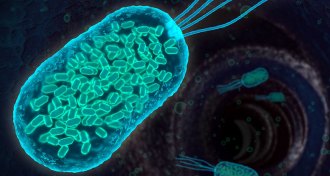 Microbes
MicrobesThese disease-fighting bacteria produce echoes detectable by ultrasound
Ultrasound can help keep tabs on genetically modified bacteria to better fight disease inside the body.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceNew 3-D printed materials harness the power of bacteria
The three-dimensional materials contain live bacteria and could generate wound dressings or clean up pollutants.
-
 Oceans
OceansIn the deep ocean, these bacteria play a key role in trapping carbon
Mysterious nitrite-oxidizing bacteria capture more carbon than previously thought and may be the primary engine at the base of the deep ocean’s food web.