Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s blood tests are getting better, but still have a ways to go
Blood biomarker tests could help doctors know if a person's cognitive symptoms are due to Alzheimer's or something else.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePsilocybin temporarily dissolves brain networks
A high dose of the psychedelic drug briefly throws the brain off kilter. Other, longer-lasting changes could hint at psilocybin's therapeutic effects.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBird flu has been invading the brains of mammals. Here’s why
Although H5N1 and its relatives can cause mild disease in some animals, these viruses are more likely to infect brain tissue than other types of flu.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBreastfeeding should take a toll on bones. A brain hormone may protect them
The hormone CCN3 improves bone strength even as breastfeeding saps bones of calcium, a study in mice shows.
By Claire Yuan -
 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Do I Know You?’ explores face blindness and the science of the mind
In her memoir, journalist Sadie Dingfelder draws on her own experiences to highlight the astonishing diversity of people’s inner lives.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePain may take different pathways in men and women
Sex differences in the function of nerve cells in mice, monkeys and humans suggest a new way to treat pain conditions.
By Claire Yuan -
 Neuroscience
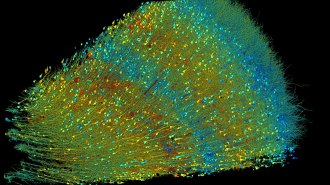
NeuroscienceBiological puzzles abound in an up-close look at a human brain
Mirror-image nerve cells, tight bonds between neuron pairs and surprising axon swirls abound in a bit of gray matter smaller than a grain of rice.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTwo distinct neural pathways may make opioids like fentanyl so addictive
A study in mice looked at how feelings of reward and withdrawal that opioids trigger play out in two separate circuits in the brain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe heart plays a hidden role in our mental health
Deciphering the messages that the heart sends to the brain could lead to new anxiety treatments and even unlock the secrets of consciousness.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow smart was T. rex?
A debate over how to count neurons in dinosaurs is raising questions about how to understand extinct animals’ behavior.
By Freda Kreier -
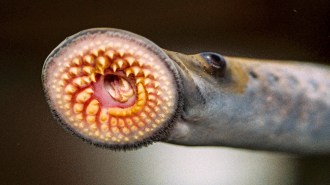 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLampreys have ‘fight or flight’ cells, challenging ideas about nervous system evolution
The discovery of sympathetic nervous system cells in lampreys draws a closer tie between the animal and complex vertebrates — such as humans.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceRat cells grew in mice brains, and helped sniff out cookies
When implanted into mouse embryos, stem cells from rats grew into forebrains and structures that handle smells.