Space
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyCosmic question mark
Two ways of measuring the universe’s expansion rate disagree by about 10 percent. One of the methods may be flawed. Or it could be that a hitherto unobserved phenomenon is at work.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyTop 10 cosmological discoveries
The cosmic microwave background radiation has played a part in many of cosmology’s greatest discoveries.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHow Earth’s radiation belt gets its ‘stripes’
The rotation of the Earth may give the planet's inner radiation belt its zebralike stripes.
-
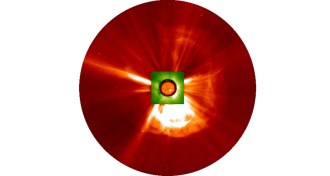 Astronomy
AstronomySun’s ejections collide to create extreme space storm
In July 2012, the sun shot off streams of charged particles and magnetic fields that collided to create a record-setting space storm.
-
 Space
SpaceExoplanet oxygen may not signal alien life
Oxygen in an exoplanet atmosphere may come from water and ultraviolet light, not alien life.
-
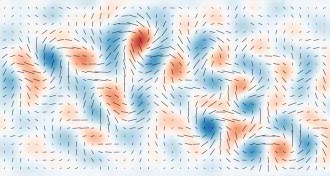 Cosmology
CosmologyGravitational waves unmask universe just after Big Bang
For the first time, researchers have seen traces of superfast cosmic expansion and gravity waves.
-
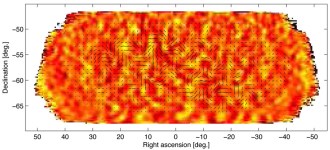 Cosmology
CosmologyInflation rides gravity waves into cosmological history
The discovery of gravity waves in the cosmic microwave radiation signals the success of inflationary cosmology.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyFirst images of gravity waves, evidence of cosmic inflation reported
The first images of gravitational waves and the first direct evidence for cosmic inflation were announced March 17.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMercury is more shriveled than originally thought
Like a week-old party balloon, Mercury has shrunk over the last 4.6 billion years.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMature galaxies found in young universe
Inactive galaxies the size of the Milky Way found dating to when the universe was just 1.5 billion years old.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBehemoth star destroys potential solar systems
A massive star in the Orion Nebula is evaporating disks surrounding young stars in its neighborhood but some disks mysteriously manage to survive.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFeedback
Readers respond to a special report on neuroscience and discuss moon dust.