All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVitamin E might limit Alzheimer’s decline
A trial of vitamin E in elderly veterans with Alzheimer’s shows promise for those in the early stages of the disease.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsNew Yorkers should relax about new roach species
Japanese roaches may be able to survive in the cold, but the added competition and their decreased allergic potential may mean the roaches’ arrival isn’t all bad.
-
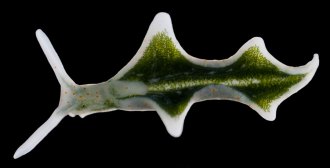 Plants
PlantsKleptoplast
A cellular part such as a light-harvesting chloroplast that an organism takes from algae it has eaten.
-
 Physics
PhysicsTea time
Leave it to the English to solve the mystery of a tea kettle’s whistle.
By Andrew Grant -
 Tech
TechReader favorites of 2013
For this issue, the editors selected the 25 most important and intriguing science stories of the year. But online readers seemed to point to a different bunch, showing just how subjective such an exercise can be.
-
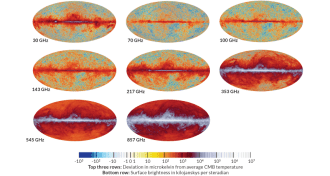 Cosmology
CosmologyBest maps of the universe, bugs and all
Maps from the European Space Agency’s Planck satellite reveal the cosmos in a range of microwave and infrared frequencies.
By Andrew Grant -

-
 Genetics
GeneticsTop genomes of 2013
Scientists continue to decode the genetic blueprints of the planet’s myriad flora and fauna.
By Beth Mole -

-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicroscopic menagerie
The microbes dwelling in and on multicellular organisms should be viewed as evolutionarily inseparable from their hosts, some biologists argue.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansMother lode
Certain sugar molecules in human breast milk do more to foster beneficial microbes, and banish harmful ones, than they do to nourish newborns.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThe vast virome
When it comes to the microbiome, bacteria get all the press. But virologists are starting to realize that their subjects also do a lot more than make people sick.