All Stories
-
 Climate
ClimateIce loss from Greenland’s glaciers may level off
Simulation suggests long-term effect on sea level not as dire as some predictions.
By Erin Wayman -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHighlights from the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting
Highlights from the pediatrics meeting held May 4-7 in Washington, D.C., include adolescent suicide risk and access to guns, a reason to let preemies get more umbilical cord blood and teens' cognitive dissonance on football concussions.
By Nathan Seppa -

-
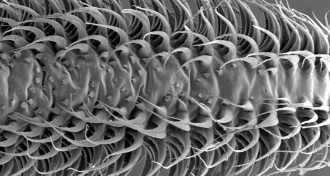 Animals
AnimalsTongue bristles help bats lap up nectar
High-speed videos capture stretched-out tongue bumps that stretch out so nectar-feeding bats can slurp up their food.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Humans
HumansGreed may breed financial fitness, but evolution allows unselfishness to survive
If greed is good, as Gordon Gekko proclaimed in the 1987 movie Wall Street, then economics ought to be a superlative science. After all, at the core of economic theory sits a greedy idealization of human nature known as Homo economicus. It’s a fictitious species that represents the individual economic agent, motivated by selfishness. H. […]
-
 Earth
EarthToxic waste sites may cause health problems for millions
Exposures to lead and chromium represent particular problems, study finds in India, Indonesia and Philippines.
By Erin Wayman -

-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPaleofantasy
What Evolution Really Tells Us about Sex, Diet, and How We Live by Marlene Zuk.
By Erin Wayman -

-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBetween Man and Beast
An Unlikely Explorer, the Evolution Debates, and the African Adventure that Took the Victorian World by Storm by Monte Reel.
By Science News -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyA Renaissance Globemaker’s Toolbox
Johannes Schöner and the Revolution of Modern Science 1474-1550 by John W. Hessler.
By Science News -
 Humans
HumansHuman ancestors had taste for meat, brains
A mix of hunting and scavenging fed carnivorous cravings of early Homo species.
By Bruce Bower