All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow two immune system chemicals may trigger COVID-19’s deadly cytokine storms
A study in mice hints at drugs that could be helpful in treating severe coronavirus infections.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThese human nerve cell tendrils turned to glass nearly 2,000 years ago
Part of a young man’s brain was preserved in A.D. 79 by hot ash from Mount Vesuvius’ eruption.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe first Denisovan DNA outside Siberia unveils a long stint on the roof of the world
Genetic evidence puts Denisovans, humankind’s now-extinct cousins, on the Tibetan Plateau from 100,000 to at least 60,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeOgre-faced spiders catch insects out of the air using sound instead of sight
A new study finds that ogre-faced spiders can hear a surprisingly wide range of sounds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow octopuses ‘taste’ things by touching
Octopus arms are dotted with cells that can "taste" by touch, which might enable arms to explore the seafloor without input from the brain.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLIGO and Virgo’s gravitational wave tally more than quadrupled in six months
Scientists report 39 sets of spacetime ripples from just half a year of data.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceDoubts over a ‘possible sign of life’ on Venus show how science works
Detecting phosphine in Venus’ atmosphere made headlines, but reanalyses and new searches call into question the original discovery of the molecule.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsGalileo’s famous gravity experiment holds up, even with individual atoms
When dropped, two types of atoms accelerate at the same rate despite their differences, much like objects in Galileo’s leaning Tower of Pisa experiment.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMummified llamas yield new insights into Inca ritual sacrifices
Bound and decorated llamas, found at an Inca site in southern Peru, may have been buried alive as part of events in annexed territories.
By Bruce Bower -
 Physics
PhysicsA photon’s journey through a hydrogen molecule is the shortest event ever timed
The shortest duration ever measured is 247 zeptoseconds, or trillionths of a billionth of a second.
-
 Space
SpaceWater exists on sunny parts of the moon, scientists confirm
New observations of the moon, made by a telescope flying onboard a Boeing 747-SP jet, have confirmed the presence of water on sunlit areas of the moon.
-
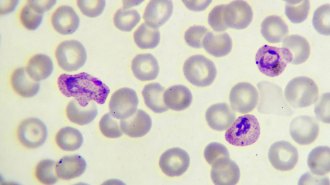 Microbes
MicrobesHow malaria parasites hide from the human immune system
By turning genes on or off, the parasite keeps blood levels low but persistent, so infection doesn’t set off alarm bells for the immune system.