All Stories
-
 Earth
EarthThere’s a new way to stop an earthquake: put a volcano in its path
An earthquake rupturing along a fault in Japan was blockaded by the magma chamber below the Mount Aso volcano, researchers propose.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient armored fish revises early history of jaws
The fossil of a 423-million-year-old armored fish from China suggests that the jaws of all modern land vertebrates and bony fish originated in a bizarre group of animals called placoderms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaph infections still a concern
Scientists have been searching for a vaccine against a deadly microbe for 50 years.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars lander silent as mission scientists work out what went wrong
Schiaparelli lander is still silent on the surface of Mars while mission scientists try to understand what happened during the probe’s descent.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceExperts don’t agree on age of Saturn’s rings
Saturn’s rings could be almost as old as the solar system, and the Cassini craft is poised to help find out.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJuno spacecraft goes into ‘safe mode,’ continues to orbit Jupiter
The Juno spacecraft has gone into safe mode while in orbit around Jupiter. Mission scientists are also closely monitoring a fuel valve issue on the probe.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsZika disrupts cellular processes to impair brain development
Discoveries about how Zika virus slows brain cell development could lead to treatments.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMission scientists await signal from Mars lander
The ExoMars mission’s Schiaparelli lander went silent before its scheduled landing on the Red Planet.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Three-parent baby’ boy healthy so far
A baby boy born with donor mitochondrial DNA seems to be healthy, researchers report at a meeting.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society2016 Nobels: Science News fans read it here first
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses Nobel-winning science and what the future may hold.
By Eva Emerson -
 Genetics
GeneticsReaders question the biology of alcoholism and more
Alcoholism-linked genes, making better corneas and more in reader feedback.
-
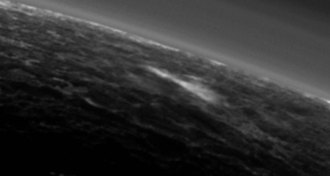 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePossibly cloudy forecast for parts of Pluto
Reflective patches on Pluto could be hints of rare cloud formation on the dwarf planet.