All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA little tablet time probably won’t fry a toddler’s brain
Good or bad, the effects tablet and smartphone use among toddlers demand more research.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMysterious bright spot on Ceres has a partner
A new image from the Dawn spacecraft finds two bright patches within a basin, possibly caused by an ice volcano.
-
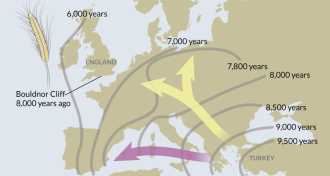 Anthropology
AnthropologyWheat reached England before farming
European hunter-gatherers may have traded for agricultural products 8,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeSexual conflict in mosquitoes may have worsened spread of malaria
Sexual conflict in Anopheles mosquitoes may have intensified their power to fuel human malaria.
By Susan Milius -
-
 Plants
PlantsBeetle RNA makes crops a noxious meal
When beetles munch plants bearing their RNA, genes the bugs need to survive are turned off.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBees may merge their flower memories
Bumblebees sometimes prefer fake flowers with the combined patterns and colors of ones seen before, suggesting they merge memories of past experiences.
-
 Life
LifeChili peppers’ pain-relieving secrets uncovered
Scientists discover how stuff that makes chili peppers hot relieves pain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome cicadas drum up a beat with the help of their wings
By using their wings as drumsticks, so-called “mute” cicadas can make themselves heard.
-
 Computing
ComputingArtificial intelligence conquers Space Invaders, Pong, Q*bert
With a single algorithm, a computer can learn dozens of classic video games, researchers from Google DeepMind in London report.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMonster black hole lurks in the early universe
A black hole weighing the same as 12 billion suns is the most massive one known in the early universe.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists confirm amassing CO2 heats Earth’s surface
Rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide increase the amount of thermal radiation striking Earth’s surface.